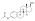A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
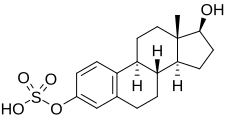
| IUPAC name
17β-Hydroxyestra-1,3,5(10)-trien-3-yl hydrogen sulfate
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1S,3aS,3bR,9bS,11aS)-1-Hydroxy-11a-methyl-2,3,3a,3b,4,5,9b,10,11,11a-decahydro-1H-cyclopentaphenanthren-7-yl hydrogen sulfate | |
| Other names
Estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol 3-sulfate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H24O5S | |
| Molar mass | 352.445 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Estradiol sulfate (E2S), or 17β-estradiol 3-sulfate,[1] is a natural, endogenous steroid and an estrogen ester.[2] E2S itself is biologically inactive,[3] but it can be converted by steroid sulfatase (also called estrogen sulfatase) into estradiol, which is a potent estrogen.[2][4][5] Simultaneously, estrogen sulfotransferases convert estradiol to E2S, resulting in an equilibrium between the two steroids in various tissues.[2][5] Estrone and E2S are the two immediate metabolic sources of estradiol.[6] E2S can also be metabolized into estrone sulfate (E1S), which in turn can be converted into estrone and estradiol.[7] Circulating concentrations of E2S are much lower than those of E1S.[1] High concentrations of E2S are present in breast tissue, and E2S has been implicated in the biology of breast cancer via serving as an active reservoir of estradiol.[2][4]
As the sodium salt sodium estradiol sulfate, E2S is present as a minor constituent (0.9%) of conjugated equine estrogens (CEEs), or Premarin.[8] It effectively functions as a prodrug to estradiol in this preparation, similarly to E1S. E2S is also formed as a metabolite of estradiol, as well as of estrone and E1S.[9][10] Aside from its presence in CEEs, E2S is not available as a commercial pharmaceutical drug.[11]
E2S shows about 10,000-fold lower potency in activating the estrogen receptors relative to estradiol in vitro.[12] It is 10-fold less potent than estrone sulfate orally in terms of in vivo uterotrophic effect in rats.[13] Estrogen sulfates like estradiol sulfate or estrone sulfate are about twice as potent as the corresponding free estrogens in terms of estrogenic effect when given orally to rodents.[14] This in part led to the introduction of conjugated estrogens (Premarin), which are primarily estrone sulfate, in 1941.[14]
Although inactive at steroid hormone receptors, E2S has been found to act as a potent inhibitor of glutathione S-transferase,[15] an enzyme that contributes to the inactivation of estradiol via conversion of it into an estradiol-glutathione conjugate.[16] As such, E2S can indirectly serve as a positive effector of estrogen signaling.[15]
Estradiol levels are about 1.5- to 4-fold higher than E2S levels in women. This is in contrast to E1S, the levels of which are about 10 to 15 times higher than those of estrone.[17]
E2S at an oral dosage of 5 mg/day in women resulted in inhibition of ovulation in 89% of cycles (47 of 53).[18]
| Estrogen | Other names | RBA (%)a | REP (%)b | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ER | ERα | ERβ | ||||
| Estradiol | E2 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| Estradiol 3-sulfate | E2S; E2-3S | ? | 0.02 | 0.04 | ||
| Estradiol 3-glucuronide | E2-3G | ? | 0.02 | 0.09 | ||
| Estradiol 17β-glucuronide | E2-17G | ? | 0.002 | 0.0002 | ||
| Estradiol benzoate | EB; Estradiol 3-benzoate | 10 | 1.1 | 0.52 | ||
| Estradiol 17β-acetate | E2-17A | 31–45 | 24 | ? | ||
| Estradiol diacetate | EDA; Estradiol 3,17β-diacetate | ? | 0.79 | ? | ||
| Estradiol propionate | EP; Estradiol 17β-propionate | 19–26 | 2.6 | ? | ||
| Estradiol valerate | EV; Estradiol 17β-valerate | 2–11 | 0.04–21 | ? | ||
| Estradiol cypionate | EC; Estradiol 17β-cypionate | ?c | 4.0 | ? | ||
| Estradiol palmitate | Estradiol 17β-palmitate | 0 | ? | ? | ||
| Estradiol stearate | Estradiol 17β-stearate | 0 | ? | ? | ||
| Estrone | E1; 17-Ketoestradiol | 11 | 5.3–38 | 14 | ||
| Estrone sulfate | E1S; Estrone 3-sulfate | 2 | 0.004 | 0.002 | ||
| Estrone glucuronide | E1G; Estrone 3-glucuronide | ? | <0.001 | 0.0006 | ||
| Ethinylestradiol | EE; 17α-Ethynylestradiol | 100 | 17–150 | 129 | ||
| Mestranol | EE 3-methyl ether | 1 | 1.3–8.2 | 0.16 | ||
| Quinestrol | EE 3-cyclopentyl ether | ? | 0.37 | ? | ||
| Footnotes: a = Relative binding affinities (RBAs) were determined via in-vitro displacement of labeled estradiol from estrogen receptors (ERs) generally of rodent uterine cytosol. Estrogen esters are variably hydrolyzed into estrogens in these systems (shorter ester chain length -> greater rate of hydrolysis) and the ER RBAs of the esters decrease strongly when hydrolysis is prevented. b = Relative estrogenic potencies (REPs) were calculated from half-maximal effective concentrations (EC50) that were determined via in-vitro β‐galactosidase (β-gal) and green fluorescent protein (GFP) production assays in yeast expressing human ERα and human ERβ. Both mammalian cells and yeast have the capacity to hydrolyze estrogen esters. c = The affinities of estradiol cypionate for the ERs are similar to those of estradiol valerate and estradiol benzoate (figure). Sources: See template page. | ||||||
| Estrogen | Structure | Ester(s) | Relative mol. weight |
Relative E2 contentb |
log Pc | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position(s) | Moiet(ies) | Type | Lengtha | ||||||
| Estradiol | – | – | – | – | 1.00 | 1.00 | 4.0 | ||
| Estradiol acetate | C3 | Ethanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 2 | 1.15 | 0.87 | 4.2 | ||
| Estradiol benzoate | C3 | Benzoic acid | Aromatic fatty acid | – (~4–5) | 1.38 | 0.72 | 4.7 | ||
| Estradiol dipropionate | C3, C17β | Propanoic acid (×2) | Straight-chain fatty acid | 3 (×2) | 1.41 | 0.71 | 4.9 | ||
| Estradiol valerate | C17β | Pentanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 5 | 1.31 | 0.76 | 5.6–6.3 | ||
| Estradiol benzoate butyrate | C3, C17β | Benzoic acid, butyric acid | Mixed fatty acid | – (~6, 2) | 1.64 | 0.61 | 6.3 | ||
| Estradiol cypionate | C17β | Cyclopentylpropanoic acid | Cyclic fatty acid | – (~6) | 1.46 | 0.69 | 6.9 | ||
| Estradiol enanthate | C17β | Heptanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 7 | 1.41 | 0.71 | 6.7–7.3 | ||
| Estradiol dienanthate | C3, C17β | Heptanoic acid (×2) | Straight-chain fatty acid | 7 (×2) | 1.82 | 0.55 | 8.1–10.4 | ||
| Estradiol undecylate | C17β | Undecanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 11 | 1.62 | 0.62 | 9.2–9.8 | ||
| Estradiol stearate | C17β | Octadecanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 18 | 1.98 | 0.51 | 12.2–12.4 | ||
| Estradiol distearate | C3, C17β | Octadecanoic acid (×2) | Straight-chain fatty acid | 18 (×2) | 2.96 | 0.34 | 20.2 | ||
| Estradiol sulfate | C3 | Sulfuric acid | Water-soluble conjugate | – | 1.29 | 0.77 | 0.3–3.8 | ||
| Estradiol glucuronide | C17β | Glucuronic acid | Water-soluble conjugate | – | 1.65 | 0.61 | 2.1–2.7 | ||
| Estramustine phosphated | C3, C17β | Normustine, phosphoric acid | Water-soluble conjugate | – | 1.91 | 0.52 | 2.9–5.0 | ||
| Polyestradiol phosphatee | C3–C17β | Phosphoric acid | Water-soluble conjugate | – | 1.23f | 0.81f | 2.9g | ||
| Footnotes: a = Length of ester in carbon atoms for straight-chain fatty acids or approximate length of ester in carbon atoms for aromatic or cyclic fatty acids. b = Relative estradiol content by weight (i.e., relative estrogenic exposure). c = Experimental or predicted octanol/water partition coefficient (i.e., lipophilicity/hydrophobicity). Retrieved from PubChem, ChemSpider, and DrugBank. d = Also known as estradiol normustine phosphate. e = Polymer of estradiol phosphate (~13 repeat units). f = Relative molecular weight or estradiol content per repeat unit. g = log P of repeat unit (i.e., estradiol phosphate). Sources: See individual articles. | |||||||||
See also
- Catechol estrogen
- DHEA sulfate
- Estradiol glucuronide
- Estriol sulfate
- Estrogen conjugate
- Lipoidal estradiol
- Pregnenolone sulfate
- List of estrogen esters § Estradiol esters
References
- ^ a b F. A. Kincl; J. R. Pasqualini (22 October 2013). Hormones and the Fetus: Volume 1: Production, Concentration and Metabolism During Pregnancy. Elsevier Science. pp. 39–. ISBN 978-1-4832-8538-2.
- ^ a b c d Peter J. O'Brien; William Robert Bruce (2 December 2009). Endogenous Toxins: Targets for Disease Treatment and Prevention, 2 Volume Set. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 869–. ISBN 978-3-527-32363-0.
- ^ Wang, Li-Quan; James, Margaret O. (2005). "Sulfotransferase 2A1 forms estradiol-17-sulfate and celecoxib switches the dominant product from estradiol-3-sulfate to estradiol-17-sulfate". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 96 (5): 367–374. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2005.05.002. ISSN 0960-0760. PMID 16011896. S2CID 24671971.
- ^ a b Jorge R. Pasqualini (17 July 2002). Breast Cancer: Prognosis, Treatment, and Prevention. CRC Press. pp. 195–. ISBN 978-0-203-90924-9.
- ^ a b IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; World Health Organization; International Agency for Research on Cancer (2007). Combined Estrogen-progestogen Contraceptives and Combined Estrogen-progestogen Menopausal Therapy. World Health Organization. pp. 279–. ISBN 978-92-832-1291-1.
- ^ G. Leclercq; S. Toma; R. Paridaens; J. C. Heuson (6 December 2012). Clinical Interest of Steroid Hormone Receptors in Breast Cancer. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 2105–. ISBN 978-3-642-82188-2.
- ^ A. T. Gregoire (13 March 2013). Contraceptive Steroids: Pharmacology and Safety. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 109–. ISBN 978-1-4613-2241-2.
- ^ Marc A. Fritz; Leon Speroff (28 March 2012). Clinical Gynecologic Endocrinology and Infertility. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 751–. ISBN 978-1-4511-4847-3.
- ^ Christian Lauritzen; John W. W. Studd (22 June 2005). Current Management of the Menopause. CRC Press. pp. 364–. ISBN 978-0-203-48612-2.
- ^ Ryan J. Huxtable (11 November 2013). Biochemistry of Sulfur. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 312–. ISBN 978-1-4757-9438-0.
- ^ King, Roberta; Ghosh, Anasuya; Wu, Jinfang (2006). "Inhibition of human phenol and estrogen sulfotransferase by certain non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents". Current Drug Metabolism. 7 (7): 745–753. doi:10.2174/138920006778520615. ISSN 1389-2002. PMC 2105742. PMID 17073578.
- ^ Coldham NG, Dave M, Sivapathasundaram S, McDonnell DP, Connor C, Sauer MJ (July 1997). "Evaluation of a recombinant yeast cell estrogen screening assay". Environ. Health Perspect. 105 (7): 734–42. doi:10.1289/ehp.97105734. PMC 1470103. PMID 9294720.
- ^ Bhavnani BR (November 1988). "The saga of the ring B unsaturated equine estrogens". Endocr. Rev. 9 (4): 396–416. doi:10.1210/edrv-9-4-396. PMID 3065072.
- ^ a b Herr, F.; Revesz, C.; Manson, A. J.; Jewell, J. B. (1970). "Biological Properties of Estrogen Sulfates". Chemical and Biological Aspects of Steroid Conjugation. pp. 368–408. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-95177-0_8 (inactive 2024-03-25). ISBN 978-3-642-95179-4.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of March 2024 (link) - ^ a b Runge-Morris MA (1997). "Regulation of expression of the rodent cytosolic sulfotransferases". FASEB J. 11 (2): 109–17. doi:10.1096/fasebj.11.2.9039952. PMID 9039952. S2CID 22112485.
- ^ Singh D, Pandey RS (1996). "Glutathione-S-transferase in rat ovary: its changes during estrous cycle and increase in its activity by estradiol-17 beta". Indian J. Exp. Biol. 34 (11): 1158–60. PMID 9055636.
- ^ Cowie, Alfred T.; Forsyth, Isabel A.; Hart, Ian C. (1980). "Growth and Development of the Mammary Gland". Hormonal Control of Lactation. Monographs on Endocrinology. Vol. 15. pp. 58–145. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-81389-4_3. ISBN 978-3-642-81391-7. ISSN 0077-1015. PMID 6250026.
- ^ Gual C, Becerra C, Rice-Wray E, Goldzieher JW (February 1967). "Inhibition of ovulation by estrogens". Am J Obstet Gynecol. 97 (4): 443–7. doi:10.1016/0002-9378(67)90555-8. PMID 4163201.
>Text je dostupný pod licencí Creative Commons Uveďte autora – Zachovejte licenci, případně za dalších podmínek. Podrobnosti naleznete na stránce Podmínky užití.
Chemical nomenclature
Chemical nomenclature#Systematic name
CAS Registry Number
Sodium
JSmol
ChEBI
ChEMBL
ChemSpider
PubChem
Unique Ingredient Identifier
CompTox Chemicals Dashboard
Q24887704#P3117
International Chemical Identifier
Simplified molecular-input line-entry system
Chemical formula
Molar mass
Standard state
Wikipedia:Chemical infobox#References
Natural product
Endogenous
Estrogen ester
Steroid sulfatase
Estradiol
Estrogen
Estrogen sulfotransferase
Chemical equilibrium
Estrone
Precursor (biochemistry)
Estrone sulfate
Breast
Breast cancer
Sodium salts
Conjugated equine estrogen
Premarin
Prodrug
Metabolite
Pharmaceutical drug
Potency (pharmacology)
Estrogen receptor
In vitro
Potency (pharmacology)
Estrone sulfate
In vivo
Uterotrophic
Potency (pharmacology)
Estrogen (medication)
Conjugated estrogens
Steroid hormone receptor
Enzyme inhibitor
Glutathione S-transferase
Enzyme
Glutathione
Conjugation (biochemistry)
Ovulation
Template:Affinities and estrogenic potencies of estrogen esters and ethers at the estrogen receptors
Template talk:Affinities and estrogenic potencies of estrogen esters and ethers at the estrogen receptors
Special:EditPage/Template:Affinities and estrogenic potencies of estrogen esters and ethers at the estrogen receptors
Estrogen (medication)
Relative binding affinity
Potency (pharmacology)
Estrogen receptor
ERα
ERβ
Estradiol (medication)
Estradiol 3-glucuronide
Estradiol 17β-glucuronide
Estradiol benzoate
Estradiol 17β-acetate
Estradiol diacetate
Estradiol 17β-propionate
Estradiol valerate
Estradiol cypionate
Estradiol palmitate
Estradiol stearate
Estrone (medication)
Estrone sulfate
Estrone glucuronide
Ethinylestradiol
Mestranol
Quinestrol
Relative binding affinity
In vitro
Radiolabel
Estradiol (medication)
Estrogen receptor
Rodent
Uterus
Cytosol
Estrogen ester
Hydrolysis
Half-maximal effective concentration
Β‐galactosidase
Green fluorescent protein
Biosynthesis
Bioassay
Yeast
ERα
ERβ
Mammal
Cell (biology)
Estradiol cypionate
Estradiol valerate
Estradiol benzoate
File:Inhibition of estradiol binding by selected estrogens, antiestrogens, and estrogen esters to human aortic tissue in vitro.png
Template:Structural properties of selected estradiol esters
Template talk:Structural properties of selected estradiol esters
Special:EditPage/Template:Structural properties of selected estradiol esters
Estradiol (medication)
File:Estradiol.svg
Estradiol acetate
File:Estradiol 3-acetate.svg
Ethanoic acid
Estradiol benzoate
File:Estradiol benzoate.svg
Benzoic acid
Estradiol dipropionate
File:Estradiol dipropionate.svg
Propanoic acid
Estradiol valerate
File:Estradiol valerate.svg
Pentanoic acid
Estradiol benzoate butyrate
File:Estradiol butyrate benzoate.svg
Benzoic acid
Butyric acid
Estradiol cypionate
File:Estradiol 17 beta-cypionate.svg
Cyclopentylpropanoic acid
Estradiol enanthate
File:Estradiol enanthate.png
Heptanoic acid
Estradiol dienanthate
File:Estradiol dienanthate.svg
Heptanoic acid
Estradiol undecylate
File:Estradiol undecylate.svg
Undecanoic acid
Estradiol stearate
File:Estradiol stearate structure.svg
Octadecanoic acid
Estradiol distearate
File:Estradiol distearate.svg
Octadecanoic acid
File:Estradiol sulfate.svg
Sulfuric acid
Estradiol glucuronide
File:Estradiol sulfate.svg
Glucuronic acid
Estramustine phosphate
File:Estramustine phosphate.svg
Normustine
Phosphoric acid
Polyestradiol phosphate
File:Polyestradiol phosphate.svg
Phosphoric acid
Ester
Carbon
Atom
Straight-chain fatty acid
Aromatic
Cyclic compound
Estrogen (medication)
Partition coefficient
Lipophilicity
Hydrophobicity
PubChem
ChemSpider
DrugBank
Polymer
Estradiol phosphate
Repeat unit
Catechol estrogen
Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate
Estradiol glucuronide
Estriol sulfate
Estrogen conjugate
Lipoidal estradiol
Pregnenolone sulfate
List of estrogen esters#Estradiol esters
ISBN (identifier)
Special:BookSources/978-1-4832-8538-2
ISBN (identifier)
Special:BookSources/978-3-527-32363-0
Doi (identifier)
ISSN (identifier)
PMID (identifier)
S2CID (identifier)
ISBN (identifier)
Special:BookSources/978-0-203-90924-9
ISBN (identifier)
Special:BookSources/978-92-832-1291-1
ISBN (identifier)
Special:BookSources/978-3-642-82188-2
ISBN (identifier)
Special:BookSources/978-1-4613-2241-2
ISBN (identifier)
Special:BookSources/978-1-4511-4847-3
ISBN (identifier)
Special:BookSources/978-0-203-48612-2
ISBN (identifier)
Special:BookSources/978-1-4757-9438-0
Doi (identifier)
ISSN (identifier)
PMC (identifier)
PMID (identifier)
Doi (identifier)
PMC (identifier)
PMID (identifier)
Doi (identifier)
PMID (identifier)
Doi (identifier)
ISBN (identifier)
Special:BookSources/978-3-642-95179-4
Template:Cite book
Category:CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of March 2024
Doi (identifier)
PMID (identifier)
S2CID (identifier)
PMID (identifier)
Doi (identifier)
ISBN (identifier)
Special:BookSources/978-3-642-81391-7
ISSN (identifier)
PMID (identifier)
Doi (identifier)
PMID (identifier)
Template:Estradiol
Template talk:Estradiol
Special:EditPage/Template:Estradiol
Estradiol
Estradiol
Estradiol (medication)
Pharmacodynamics of estradiol
Pharmacokinetics of estradiol
Estrogen
Estrogen (medication)
Hormone replacement therapy
Feminizing hormone therapy
Estradiol-containing birth control pill
Combined injectable birth control
High-dose estrogen
Hydroxylation of estradiol
Estrogen ester
Estradiol acetate
Estradiol acetylsalicylate
Estradiol anthranilate
Estradiol benzoate butyrate
Estradiol benzoate cyclooctenyl ether
Estradiol benzoate
Estradiol butyrylacetate
Estradiol cyclooctyl acetate
Estradiol cypionate
Estradiol decanoate
Estradiol diacetate
Estradiol dibutyrate
Estradiol dienantate
Estradiol dipropionate
Estradiol distearate
Estradiol disulfate
Estradiol diundecylate
Estradiol diundecylenate
Estradiol enantate
Estradiol furoate
Estradiol glucuronide
Estradiol hemisuccinate
Estradiol hexahydrobenzoate
Estradiol monopropionate
Estradiol mustard
Estradiol palmitate
Estradiol phenylpropionate
Estradiol phosphate
Estradiol pivalate
Estradiol propoxyphenylpropionate
Estradiol salicylate
Estradiol stearate
Estradiol sulfamate
Estradiol undecylate
Estradiol undecylenate
Estradiol valerate
Estramustine phosphate
Estrogen ester
Polyestradiol phosphate
Estrone (medication)
Estriol (medication)
Estetrol (medication)
Ethinylestradiol
Conjugated estrogens
Esterified estrogens
Estrone sulfate (medication)
Estropipate
Template:Steroid hormones
Template talk:Steroid hormones
Special:EditPage/Template:Steroid hormones
Endogenous
Steroid
Precursor (chemistry)
Cholesterol
22R-Hydroxycholesterol
20α,22R-Dihydroxycholesterol
Pregnenolone
17α-Hydroxypregnenolone
21-Hydroxypregnenolone
Corticosteroid
Glucocorticoid
Tetrahydrocorticosterone
5α-Dihydrocorticosterone
11-Deoxycorticosterone
11-Deoxycortisol
11-Ketoprogesterone
21-Deoxycortisol
21-Deoxycortisone
Corticosterone
Cortisol
Cortisone
17α-Hydroxypregnenolone
17α-Hydroxyprogesterone
Pregnenolone
Progesterone
Updating...x
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok.
Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky
použitia.