A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
| Lehigh Valley | |
|---|---|
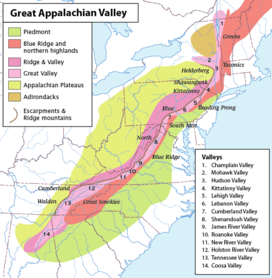 The Great Appalachian Valley includes the Lehigh Valley (5) depicted south of the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians and between the Lebanon (6) and Kittatinny (4) valleys. | |
| Geography | |
| Location | Lehigh County Northampton County |
| Population centers | Allentown, Bethlehem, Easton |
| Borders on | Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians Blue Mountain (north) South Mountain (south) Delaware River (east) Lebanon Valley (west) |
The Lehigh Valley (/ˈliːhaɪ/), known colloquially as The Valley, is a geographic region formed by the Lehigh River in Lehigh County and Northampton County in eastern Pennsylvania. It is a component valley of the Great Appalachian Valley bound to the north by Blue Mountain, to the south by South Mountain, to the west by Lebanon Valley, and to the east by the Delaware River on Pennsylvania's eastern border with Warren County, New Jersey and the Skylands Region.[1] The Valley is about 40 miles (64 km) long and 20 miles (32 km) wide.[2] The Lehigh Valley's largest city is Allentown, the third largest city in Pennsylvania and the county seat of Lehigh County, with a population of 125,845 residents as of the 2020 census.[3]
The Allentown-Bethlehem-Easton metropolitan area, which includes the Lehigh Valley, is currently Pennsylvania's third most populous metropolitan area after those of Philadelphia and Pittsburgh, and the nation's 68th largest metropolitan area with a population of 861,889 residents as of 2020. Lehigh County is among Pennsylvania's fastest-growing counties, and the Lehigh Valley leads Pennsylvania in terms of population growth in the 18-to-34 year old demographic.[4] The region's core population centers are located in southern and central Lehigh and Northampton counties along Interstate 78, Interstate 476, Pennsylvania Route 309, and U.S. Route 22.
The Lehigh Valley has played a sizable and influential role in the country's founding and history. On June 21, 1774, patriots in the region were among the first to organize in opposition to British colonial governance, demanding formation of the First Continental Congress and establishing one of the colonies' first patriot militias that drove Loyalists out of the region and provided early resistance to British colonial governance.[5] The Lehigh Valley helped inspire and then supported the Revolutionary War, establishing one of the first hospitals for treatment of wounded Continental Army troops at the Allentown location now occupied by the Farr Building. Washington and his commanders established two POW camps in Allentown, one at 8th and Hamilton Streets and another on Gordon Street, to house Hessian mercenaries captured at the Battle of Trenton,[6] and Washington visited the region following the Battle of Trenton and several additional times during and following the Revolution.[7] Allentown also played a historical role in protecting the Liberty Bell from British capture following the September 26, 1777 fall of Philadelphia to the British Army, concealing the bell for nine months from September 1777 to June 1778 under floor boards in Allentown's Zion Reformed Church, an act that was later commemorated in 1962 with the establishment of the Liberty Bell Museum inside this Allentown church.
In the 19th century, significant numbers of Lehigh Valley volunteers contributed to the Union's preservation during the American Civil War. In the war's first days, following the April 13, 1861 fall of Fort Sumpter, Allen Infantry, a militia of volunteers from Allentown and its surrounding communities, responded to Lincoln's April 15, 1861 proclamation by deploying in defense of the national capital of Washington, D.C.[8] Four months later, in August 1861, Allen Infantry and other large numbers of Allentown-area volunteers formed Pennsylvania's 47th Regiment, which bolstered the Union Army's strength, helping lead the Union's military victories in the Battle of St. Johns Bluff and later participated in daring raids against Confederate positions in the Deep South, including in the 1864 Red River campaign in the Trans-Mississippi theater.[8]
Throughout the 19th and most of the 20th centuries, the Lehigh Valley's leadership in coal and iron mining and then in its 20th century leadership in steel and other heavy manufacturing proved central to the nation's industrialisation, contributing sizably to the American Industrial Revolution and the nation's rise as a global manufacturing and economic superpower. Lehigh Canal, whose construction began in 1818, permitted the Lehigh Valley to begin transporting mined coal and iron and ultimately steel components and products through the Lehigh River, a 109-mile-long (175 km) tributary of the Delaware River for which the Valley is named, to the nation's largest markets in New York City, Philadelphia, New Jersey, and elsewhere. Many Lehigh Valley companies contributed to the region's development as a global industrial leader, including Bethlehem Steel, which grew to become one of the world's largest and most prominent manufacturers of steel in the 20th century. But the company later experienced a rapid downfall beginning in the early 1980s that included major layoffs and production cutbacks that worsened steadily, forcing the company into bankruptcy protection in 2001 and dissolution in 2003.
As of 2020, the Lehigh Valley's total gross domestic product (GDP) is $42.9 billion, driven by more diverse industry sector contributions, including from its finance, manufacturing, health care and education, and information industry sectors, compared to its heavy manufacturing focus of the 20th century. The Valley is one of Pennsylvania's largest and fastest growing economies, experiencing 5% GDP growth between 2016 and 2017 alone.[9] The region's primary commercial airport is Lehigh Valley International Airport; the airport's air traffic has grown considerably in the 21st century fueled by considerable increases in air cargo traffic, which exceeded 210 million pounds in 2016.[10][11]
The Lehigh Valley is located within the U.S. Northeast megalopolis with ease of access and close proximity to many of the nation's largest population centers, airports, terminals, railways, and seaports, including New York City, which is 90 miles (140 km) to its east, and Philadelphia, which is 60 miles (97 km) to its southeast. The region is located geographically within a one-day drive to over a third of the U.S. population and over half of Canada's population, which has proven a helpful factor behind the region's 21st emergence as a national leader in warehousing, logistics, manufacturing, and distribution. Gains in these and other industry sectors in the Valley have helped offset the significant losses the region experienced from its late 20th century decline in heavy manufacturing. Since its settlement in the 1700s, the Lehigh Valley has been the birthplace or home to several notable Americans who have proven influential across a broad range of fields, including academia, art and music, business, government and politics, the military, professional and Olympic-level athletics, and other fields.
History


The Lehigh Valley was settled in the first half of the 1700s by predominantly German immigrants fleeing war and religious oppression. Prior to their arrival, the region was inhabited by Lenape Indian tribes who hunted, fished, and quarried jasper in the region. Sons of provincial Pennsylvania founder William Penn acquired much of the Lehigh Valley in the Walking Purchase in 1737 during the colonial period. Lenape Indians subsequently retaliated with raids against European settlers throughout the 1750s and early 1760s but were moved out of the region by the mid-1760s. The region was initially established in 1682 as part of Bucks County. In 1752, the region became part of Northampton County, and Lehigh County was later separated from Northampton County and formally established in 1812.[12] Shelter House in Emmaus, constructed in 1734 by Pennsylvania German settlers, is the oldest still-standing building structure in the Lehigh Valley and believed to be one of the oldest in the state.[13]
American Revolutionary War
Allentown and its surrounding communities played an important and historic role in the emergence of the American Revolution. Some of the first resistance to British colonialism began in Allentown and surrounding Lehigh County communities in the Lehigh Valley. As early as June 21, 1774, patriot forces in Allentown began meeting to formulate resistance plans to British colonial governance. On December 21, 1774, a Committee of Observation was formally established by Allentown-area patriot militias.[5]
Following the signing of the Declaration of Independence, the Colonial British government in Allentown began dissolving and these patriot militias ceased control, pressuring Tories out of the region. Washington and his Continental Army staff passed through Allentown following their victory at the Battle of Trenton, traveling up Lehigh Street, which was then called Water Street. Washington and his staff stopped at the foot of Lehigh Street at a large spring on what today is the property occupied by Wire Mill. They rested there, watered their horses, and then proceeded to their post of duty.[14] Allentown supported the Revolution, establishing the first hospitals for treatment of wounded Continental Army troops at various city locations, including at the current location of the Farr Building at 739 Hamilton Street.
Washington and his commanders also chose to establish two POW camps in Allentown, one at 8th and Hamilton Streets and another on Gordon Street, to house Hessian mercenaries captured at the Battle of Trenton.[6] In addition to visiting Allentown after his victory at the Battle of Trenton, Washington returned to the city and region several additional times during and following the Revolution.[7]
Allentown also played a historical role in protecting the Liberty Bell from British capture following the September 26, 1777 fall of Philadelphia to the British Army, concealing the Liberty Bell for nine months from September 1777 to June 1778 under floor boards in Allentown's Zion Reformed Church. After Washington and the Continental Army's defeat at the Battle of Brandywine on September 11, 1777, the revolutionary capital of Philadelphia was left defenseless and Pennsylvania's Supreme Executive Council, anticipating Philadelphia's fall, ordered that eleven Philadelphia bells, including the Liberty Bell (then known as the State House Bell), be taken down and moved to present day Allentown (then called Northamptontown). Once arriving in Allentown, the Liberty Bell and other bells were hidden under floor boards at Zion Reformed Church on West Hamilton Street to protect them from being seized and melted down by the British Army for use as munitions.
In 1962, inside this still-standing church at 622 West Hamilton Street in Allentown, the Liberty Bell Museum was opened to commemorate this successful concealment of the Liberty Bell in Allentown during the American Revolution.
American Civil War
The region again proved influential in the American Civil War. Following the Union Army's defeat at the Battle of Fort Sumter and Lincoln's April 15, 1861 proclamation calling for state militia to provide 75,000 volunteers to defend the national capital in Washington, D.C., Allentown immediately deployed its Allen Infantry, which defended Washington, D.C. from Confederate attack following Fort Sumter's fall. Also known as the Allen Guards, the Allen Infantry mustered in for duty on April 18, 1861. As the Civil War progressed, members of this unit and other Lehigh Valley volunteers formed and assimilated into the 47th Pennsylvania Infantry Regiment, which proved influential in expanding the Union Army's reach into the Deep South, permitting it to launch successful attacks against Confederate positions in the Battle of St. Johns Bluff in 1862 and throughout the Red River campaign in the Trans-Mississippi theater in 1864. These victories tipped the Civil War in the Union's favor.[8] On October 19, 1899, a monument in honor of the Lehigh Valley men killed in their volunteer service to the Union's preservation, the Soldiers and Sailors Monument was erected at Seventh and Hamilton Streets in Center City Allentown, where it still stands.[15]
Industrial Revolution

The opening of the Lehigh Canal in 1827 contributed significantly to transforming Allentown and the Lehigh Valley from a rural agricultural area dominated by German-speaking people into one of the nation's first urbanized industrialized areas. The Lehigh Valley underwent significant industrialization throughout the 19th and most of the 20th centuries and was a major manufacturing hub in the American Industrial Revolution.
The Lehigh Valley is named for the Lehigh River, which runs through the region. It owes much of its development and history to anthracite coal, timber, and ore that was only commerically possible with the development of the Lehigh Canal and the Lehigh Valley's extensive railway infrastructure that permitted these minerals and later the region's manufactured steel to be transported for sale in major national and overseas markets. The Lehigh Canal operated into the Great Depression, feeding ports up and down the Delaware River, the Pennsylvania Canal, and transoceanic demand, and was integral to the industrialization of the greater Delaware Valley region. The Morris Canal, the 22–23 miles (35–37 km) anthracite coal feeder of the Delaware and Raritan Canal. and locks at New Hope on the Delaware Canal were built to fuel anthracite energy needs of Trenton, Newark, Jersey City, and New York City.
In 1899, Bethlehem Steel was formed in Bethlehem in the Lehigh Valley. The company developed into the nation's second largest manufacturer of steel, and its steel was used in developing many of the nation's earliest and largest infrastructure and building projects, including the Empire State Building, Madison Square Garden, and Rockefeller Center in New York City, Merchandise Mart in Chicago, the George Washington, Verrazzano, and Golden Gate Bridges, and warships and other military equipment that proved essential in American-led victories in both World Wars.[16] The company's ascent during the 20th century was very prominently associated with the emergence of the U.S. as both a world leader in global manufacturing and as the world's largest economy, and its demise has sometimes been pointed to as one of the nation's most prominent first stumbling points in the face of foreign competition and other economic challenges that emerged in the late 20th century and contributed to the nation's emergence of its Rust Belt.
Following nearly a century of global leadership, growth, and profitability in steel manufacturing, Bethlehem Steel abruptly reported operating losses of $1.5 billion in 1982, citing foreign competition from Asian economies and costly U.S. governmental regulations and labor costs for the losses. The company abruptly reduced operations, resulting in considerable Lehigh Valley layoffs and a dramatic related economic downturn in the region.[17] The company continued functioning on a vastly reduced scale for a period, but ultimately ceased steel manufacturing entirely at its primary Bethlehem manufacturing plant in 1995. In 2001, the company filed for bankruptcy protection and, in 2003, the company was dissolved. In the late 20th and early 21st centuries, the downturn and ultimate demise of Bethlehem Steel, once one of the most iconic and prominent symbols of American global economic power and leadership, emerged as an example cited by those who believe American global economic leadership is now in either gradual or even rapid descent.[18]
Geography
The Lehigh Valley is geologically and geographically part of the Great Appalachian Valley, a geographic region made up of limestone that stretches along the eastern edge of the Appalachian Mountains. The Lehigh Valley is so named because it is located geographically within an actual valley formed by the Lehigh River that lies between two mountain ridges, Blue Mountain in the Valley's north and South Mountain in the Valley's south.[2] The Lehigh Valley is the lower part of the drainage basin of the Lehigh River.[19]
Cities and location


The Lehigh Valley has three principal cities: Allentown, Bethlehem, and Easton. The region is located between two of the nation's largest population centers, 90 miles (140 km) west of New York City, the nation's largest and world's 30th largest city, and 60 miles (97 km) north of Philadelphia, the nation's sixth largest and world's 67th largest city.
The region borders Carbon County and the Coal Region to its north, the Delaware River and Warren County, New Jersey to its east, Bucks and Montgomery Counties in suburban Philadelphia to its south, and Berks and Schuylkill Counties to its west.
Municipalities with more than 10,000 people
- Allentown (125,845)
- Bethlehem (75,781)
- Bethlehem Township (23,952)
- Easton (28,127)
- Emmaus (11,616)
- Forks Township (15,417)
- Hanover Township (Northampton) (11,575)
- Lehigh Township (10,419)
- Lower Macungie Township (31,964)
- Lower Saucon Township (10,813)
- Northampton (10,395)
- North Whitehall Township (15,655)
- Palmer Township (21,469)
- Salisbury Township (13,763)
- South Whitehall Township (19,794)
- Upper Macungie Township (25,797)
- Upper Saucon Township (16,462)
- Whitehall Township (27,423)
Municipalities with fewer than 10,000 but more than 5,000 people
Municipalities with fewer than 5,000 people
- Alburtis
- Allen Township
- Bath
- Chapman
- Coopersburg
- Coplay
- East Allen Township
- East Bangor
- Fountain Hill
- Freemansburg
- Glendon
- Hanover Township (Lehigh)
- Heidelberg Township
- Lower Milford Township
- Lower Mount Bethel Township
- Lowhill Township
- Lynn Township
- Macungie
- North Catasauqua
- Pen Argyl
- Portland
- Roseto
- Slatington
- Stockertown
- Tatamy
- Walnutport
- Weisenberg Township
- West Easton
- Wind Gap
Census-designated places and villages
- Ackermanville
- Ancient Oaks
- Balliettsville
- Beersville
- Belfast
- Berlinsville
- Best Station
- Breinigsville
- Butztown
- Cementon
- Center Valley
- Cetronia
- Cherryville
- Chestnut Hill
- Chickentown
- Christian Springs
- Colesville
- Danielsville
- DeSales University
- Dorneyville
- Eagle Point
- Eastlawn Gardens
- East Texas
- Egypt
- Emanuelsville
- Emerald
- Flicksville
- Fogelsville
- Franks Corner
- Friedensville
- Fullerton
- Gauff Hill
- Germansville
- Hanoverville
- Hensingersville
- Hokendauqua
- Hollo
- Hosensack
- Ironton
- Jacksonville
- Katellen
- Klecknersville
- Kuhnsville
- Lanark
- Laurys Station
- Limeport
- Locust Valley
- Lynnport
- Martin's Creek
- Mickleys
- Middletown
- Moorestown
- Morgan Hill
- Mount Bethel
- Neffs
- Newburg
- New Smithville
- New Tripoli
- Old Orchard
- Old Zionsville
- Orefield
- Palmer Heights
- Pleasant Corners
- Powder Valley
- Raubsville
- Scherersville
- Schnecksville
- Schoenersville
- Seidersville
- Shimerville
- Sigmund
- Slatedale
- Slateford
- Stiles
- Summit Lawn
- Trexlertown
- Treichlers
- Vera Cruz
- Walbert
- Wanamakers
- Wassergass
- Werleys Corner
- Wescosville
- West Catasauqua
- Zionsville
- Zucksville
Metropolitan and Combined Statistical Areas
Allentown–Bethlehem–Easton, PA–NJ Metropolitan Statistical Area | |
|---|---|
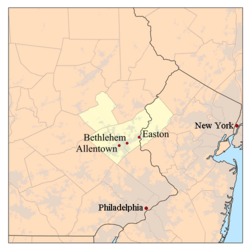 Map of the Allentown-Bethlehem-Easton, PA-NJ Metro Area | |
| Country | |
| States | |
| Principal cities | Allentown Bethlehem Easton |
| Rank | 68th |
| Area | |
| • Total | 3,760 km2 (1,453 sq mi) |
| Population (2020 U.S. Census) | |
| • Total | 861,889[21] |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (ET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Area code(s) | 610, 484, and 908 |
The Allentown-Bethlehem-Easton, PA-NJ Metropolitan Statistical Area is a Metropolitan Statistical Area that includes Carbon County in the Coal Region, Lehigh and Northampton counties in eastern Pennsylvania, and Warren County in the Skylands region of northwest New Jersey.[20][22] As of the 2020 census, it is the 68th largest metropolitan area in the nation with a population of 861,889.[23]
Climate
The Lehigh Valley has four distinct seasons, which typically include hot and humid summers, cold winters, and short and mild springs and falls. It has a humid continental climate (Dfa/Dfb) and the hardiness zone ranges from 5b in higher elevation locations in northern Carbon County to 6b (the principal zone in Lehigh, Northampton, and southern Warren Counties).[24] The 1991-2020 hardiness zone for the airport and lower elevations is 7b.
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Record high °F (°C) | 72 (22) |
81 (27) |
87 (31) |
93 (34) |
97 (36) |
100 (38) |
105 (41) |
100 (38) |
99 (37) |
93 (34) |
81 (27) |
72 (22) |
105 (41) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 60 (16) |
61 (16) |
71 (22) |
83 (28) |
89 (32) |
93 (34) |
95 (35) |
93 (34) |
89 (32) |
80 (27) |
71 (22) |
62 (17) |
96 (36) |
| Average high °F (°C) | 38.4 (3.6) |
41.6 (5.3) |
50.8 (10.4) |
63.4 (17.4) |
73.5 (23.1) |
81.9 (27.7) |
86.4 (30.2) |
84.3 (29.1) |
77.4 (25.2) |
65.5 (18.6) |
53.8 (12.1) |
43.1 (6.2) |
63.3 (17.4) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 30.1 (−1.1) |
32.4 (0.2) |
40.7 (4.8) |
51.8 (11.0) |
62.0 (16.7) |
70.9 (21.6) |
75.6 (24.2) |
73.6 (23.1) |
66.3 (19.1) |
54.6 (12.6) |
43.9 (6.6) |
35.0 (1.7) |
53.1 (11.7) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 21.8 (−5.7) |
23.2 (−4.9) |
30.5 (−0.8) |
40.3 (4.6) |
50.6 (10.3) |
59.9 (15.5) |
64.7 (18.2) |
62.8 (17.1) |
55.2 (12.9) |
43.8 (6.6) |
34.1 (1.2) |
26.8 (−2.9) |
42.8 (6.0) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 4 (−16) |
6 (−14) |
14 (−10) |
26 (−3) |
35 (2) |
47 (8) |
54 (12) |
51 (11) |
40 (4) |
29 (−2) |
19 (−7) |
12 (−11) |
2 (−17) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −15 (−26) |
−12 (−24) |
−5 (−21) |
12 (−11) |
28 (−2) |
39 (4) |
46 (8) |
41 (5) |
30 (−1) |
21 (−6) |
3 (−16) |
−8 (−22) |
−15 (−26) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 3.30 (84) |
2.77 (70) |
3.63 (92) |
3.67 (93) |
3.65 (93) |
4.40 (112) |
5.30 (135) |
4.56 (116) |
4.84 (123) |
4.14 (105) |
3.24 (82) |
3.86 (98) |
47.36 (1,203) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 9.8 (25) |
10.8 (27) |
6.3 (16) |
0.5 (1.3) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.2 (0.51) |
0.9 (2.3) |
4.6 (12) |
33.1 (84) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 11.4 | 10.1 | 10.9 | 11.8 | 12.4 | 11.4 | 11.0 | 10.2 | 9.6 | 9.9 | 8.9 | 11.5 | 129.1 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 5.1 | 4.3 | 2.6 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 2.9 | 15.7 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 70 | 66 | 62 | 61 | 66 | 68 | 70 | 72 | 74 | 72 | 70 | 71 | 69 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 43 | 48 | 53 | 47 | 54 | 63 | 57 | 56 | 54 | 53 | 45 | 42 | 51 |
| Source: NOAA (relative humidity 1981–2010)[25][26][27] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1900 | 231,341 | — | |
| 1910 | 289,686 | 25.2% | |
| 1920 | 346,664 | 19.7% | |
| 1930 | 391,516 | 12.9% | |
| 1940 | 396,673 | 1.3% | |
| 1950 | 437,824 | 10.4% | |
| 1960 | 545,057 | 24.5% | |
| 1970 | 594,124 | 9.0% | |
| 1980 | 635,481 | 7.0% | |
| 1990 | 686,688 | 8.1% | |
| 2000 | 740,395 | 7.8% | |
| 2010 | 821,623 | 11.0% | |
| 2020 | 861,889 | 4.9% | |
The Lehigh Valley has a total population of 861,889 residents as of the 2020 U.S. census, making it the third largest metropolitan area in Pennsylvania and 68th largest metropolitan area in the nation.[28]
According to the 2018 American Community Survey conducted by the U.S. Census Bureau, 87.1% of the Lehigh Valley's population was White American, 4.6% was Black or African American, 0.1% was American Indian, 2.3% was Asian American, 0.1% was Native Hawaiian, 0.1% were Pacific Islander Americans, 4.3% were of some other race, and 1.5% belonged to two or more races. Hispanics and Latinos of any race made up 11.3% of the population and represent the Lehigh Valley's fastest-growing demographic. Lehigh County is in the top 1% of all U.S. counties for inward migration from international locations, according to Select USA, a U.S. Department of Commerce program.[4] The Lehigh Valley as a whole leads Pennsylvania in terms of population growth in the 18-to-34 year old demographic, according to 2020 census data.[4]
The Lehigh Valley's population growth is partly a result of a growing influx of residents from New Jersey and New York seeking to take advantage of the region's lower cost of living, its employment opportunities, and its close proximity to two of the largest cities in the country, Philadelphia and New York City. The Valley's population is expected to increase by 227,000 people by 2040, making it one of the fastest-growing areas in the state and nation.[29]
| County | 2021 Estimate | 2020 Census | Change | Area | Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lehigh County | 375,539 | 374,557 | +0.26% | 345 sq mi (890 km2) | 1,089/sq mi (420/km2) |
| Northampton County | 313,628 | 312,951 | +0.22% | 370 sq mi (960 km2) | 848/sq mi (327/km2) |
| Warren County | 110,731 | 109,632 | +1.00% | 356.92 sq mi (924.4 km2) | 310/sq mi (120/km2) |
| Carbon County | 65,412 | 64,749 | +1.02% | 381 sq mi (990 km2) | 172/sq mi (66/km2) |
| Total MSA Population | 865,310 | 861,889 | +0.40% | 1,452.92 sq mi (3,763.0 km2) | 596/sq mi (230/km2) |
Median household income for the region increased from $57,288 to $62,507 between 2015 and 2019.[30]
Economy



The Lehigh Valley's economy has been known historically and globally for its leadership throughout the 19th and 20th centuries in heavy manufacturing. Beginning in the 1980s, however, the region's manufacturing sector declined rapidly as a result of foreign competition, trade practices, operational costs, regulations, and other factors. The most prominent example was the plight of Bethlehem Steel, once the nation's second largest manufacturer of steel. Headquartered in Bethlehem, Bethlehem Steel suspended most of its operations in the early 1980s and ultimately declared bankruptcy in 2001 and was dissolved in 2003.
Since the late 20th century, the Lehigh Valley has begun to recover from the loss of its once powerful manufacturing base and other industry sectors have emerged in the region, providing a more diversified regional economy. As of 2020, the Valley's top five industries were: 1.) finance, 2.) manufacturing, 3.) health care and education, 4.) professional and business services, and 5.) information. Other major industry sectors in the area include transportation, retail trade, and restaurants and hospitality. As of 2020, the Lehigh Valley's total gross domestic product was $42.9 billion.[31]
Bethlehem Steel
The Lehigh Valley is known historically for its production of steel, Portland cement, silk, and apparel. Bethlehem Steel, founded in 1899 and based in Bethlehem, was a foundation of the Lehigh Valley's economy for nearly a century from 1899 through the early 1980s. At the pinnacle of its success, Bethlehem Steel was the nation's second largest and one of the world's largest steel manufacturers. Bethlehem Steel was instrumental in the development of many of the nation's most prominent 20th century infrastructure projects. Its steel was used to build 28 Liberty Street, Chrysler Building, the Empire State Building, Madison Square Garden, Rockefeller Center, and the Waldorf Astoria hotel in New York City and Merchandise Mart in Chicago. Among major bridges, the company's steel was used to construct the George Washington Bridge and Verrazzano-Narrows Bridge in New York City, the Golden Gate Bridge in San Francisco, and the Peace Bridge between Buffalo and Fort Erie, Ontario. The Roosevelt administration relied heavily on Bethlehem Steel during World War II, utilizing the company to produce the steel necessary for shipbuilding, ammunition, and other military equipment that proved essential to the Allies' ability to prevail in these conflicts.
In the late 20th century, however, a variety of factors, including the practices of foreign competitors, began eroding Bethlehem Steel's once historical global leadership in steelmaking. In 1982, the company announced it was discontinuing most of its operations. In 2001, the company declared bankruptcy. In 2003, it was dissolved. Throughout the late 20th century, other heavy manufacturing companies in the Lehigh Valley that once served as backbones for the region's economy suffered similarly, either downsizing significantly or dissolving, which destabilized the region considerably.
In the early 2000s, seeking to replace the heavy manufacturing companies that had been the region's foundation for decades, the Lehigh Valley began developing other economic sectors, including financial services, health care, life sciences, and technology. The Lehigh Valley also began emerging as a national warehouse and distribution hub, largely due to its proximity to many of the largest U.S. markets and relatively lower operating costs compared to other Northeast U.S. regions.[32] More recently, a movement to reestablish manufacturing activities in the U.S., driven by customer demand for American-made products, faster product delivery, increased overseas wages, and inflated costs and extended timeframes for shipping has led to some renewed growth in the Valley's manufacturing sector.[33] Several large companies from China and Germany have invested tens of millions of dollars into developing significant operations in the Lehigh Valley, which has generated thousands of new jobs in the region.[34]
Largest employers
As of 2019, the Lehigh Valley's top five employers are: 1.) Lehigh Valley Health Network, 2.) St. Luke's Hospital and Health Network, 3.) Amazon, 4.) Lehigh Valley Physician Group, and 5.) Mack Trucks.[35]
Business and economic environment
The Lehigh Valley is one of the fastest-growing and largest economies in Pennsylvania with a total GDP of $43.8 billion that saw a five percent increase between 2016 and 2017 alone driven by strong manufacturing, financial, health care, and professional services industry segments.[36] It is centrally located in the Northeast megalopolis with ease of access and close proximity to several of the largest U.S. markets, population centers, airports, terminals, railways, and seaports, including the New York City and Philadelphia metropolitan areas. The Lehigh Valley is within a one-day drive to over a third of the U.S. population and to over half the population of Canada.[37][38] The Valley has a lower cost of living, more affordable real estate, lower taxes, and a larger and more affordable labor pool than many other Northeastern U.S. metropolitan regions.[39] These attributes and others, including sizable investments in business development incentive programs and a friendlier regulatory environment, provide the area with a comparatively favorable business climate compared to surrounding metropolitan areas.[40][38][41][42][43][44]
Due in large part to this comparably favorable business climate and mature business support programs,[45] the Lehigh Valley has been very successful in luring established businesses as well as new startup companies from higher cost areas such as New York and New Jersey, generating thousands of new jobs and significant new investments in the region.[40][46] Large companies such as Amazon.com have praised the Lehigh Valley for its commitment to business support, infrastructure investment, and incentive programs, citing these as major reasons for their continuing expansions and increased hiring in the region[47][48] and Allegiant Air, a low-cost budget airline, opened a new flight base at the Lehigh Valley International Airport in February 2020, noting the area's rapid growth, lower operational business costs, and its proximity to popular destinations as significant reasons for expanding their Lehigh Valley International Airport flights.[49]
Other large national and international companies either based in the Lehigh Valley or with significant operations there include Broadcom Corporation (in Allentown), Avantor Performance Materials (in Allentown), Air Products (in Trexlertown), Crayola (in Easton), Buckeye Partners (in Emmaus), HeidelbergCement (in Fogelsville), Just Born (in Bethlehem, maker of Peeps candies), Mack Trucks (in Allentown), Martin Guitar (in Nazareth), Olympus Corporation (in Center Valley), OraSure Technologies (in Bethlehem), PPL Corporation (in Allentown), Wind Creek Bethlehem (in Bethlehem), Dun & Bradstreet (in Center Valley), Victaulic (in Easton), and others.
The Lehigh Valley was recognized by business publication Site Selection Magazine in 2014, 2017, 2018, and again in 2019 as being the second-best performing region of its size for economic development in the nation and the best performing region in the entire Northeast U.S..[50] It was ranked by Fortune in 2015 as one of the top 10 best places in the U.S. to locate corporate finance and information technology operations, including call and IT support centers.[51][52] Allentown, the Lehigh Valley's largest city, was cited as a "national success story" in April 2016 by the Urban Land Institute for its downtown redevelopment and transformation that has led to $1 billion worth of new development projects there between 2015 and 2019, one of only six communities nationally to achieve this distinction.[53][54]
The Lehigh Valley is one of the leading areas on the East Coast for warehouses and distribution centers. Because of this, it is sometimes referred to as the nation's "second Inland Empire" for freight.[55] Large national companies that own and operate warehouses and distribution centers in the Lehigh Valley include Amazon.com, B. Braun, Boston Beer Company (brewer of Samuel Adams brand beer), BMW, Bridgestone, FedEx SmartPost, FedEx Ground, Home Depot, J. C. Penney, Nestlé Purina, ShopRite, Stitch Fix, The Coca-Cola Company, Ocean Spray, Phillips Pet Food and Supplies, True Value, Uline, Zulily, and others. Most of these warehouses and distribution centers are located along the Valley's southern U.S. Route 22, Interstate 78, and Interstate 476 corridors, which provide direct access to numerous major markets throughout the Northeast U.S. and beyond.
In 2018, due to this direct access and proximity to major markets, FedEx Ground constructed their largest distribution hub in the country in the Lehigh Valley near Lehigh Valley International Airport. This new hub can process up to 45,000 packages per hour and currently employs over 2,000 people. By 2030, it is expected to have a total size of 1,100,000 square feet (100,000 m2) square feet and employ over 3,000 people.[56] It opened in September 2018 at a cost of $335 million to build.[57]
The Boston Beer Company operates its largest U.S. production brewery facility in Breinigsville in the Lehigh Valley, which produces over 2/3rds of all Samuel Adams beer globally. The company continues to upgrade and expand operations at this facility and has cited the location as central to its overall corporate success.[58] Additionally, Ocean Spray, a popular maker of juice drinks and other fruit products, produces 40 percent of its total national beverage volume at its Lehigh Valley plant in Breinigsville.[59] Due to Pennsylvania's lack of an excise tax on cigars and the Lehigh Valley's close proximity to major markets, the region is home to some of the nation's largest cigar distributors and retailers.[60]
Retail shopping
The Lehigh Valley has several retail establishments. The largest is the Pennsylvania Route 145/MacArthur Road Corridor, just north of Allentown, which is anchored by Lehigh Valley Mall and Whitehall Mall.
Other Lehigh Valley malls include Palmer Park Mall in Easton, South Mall in South Whitehall Township, and Westgate Mall in Bethlehem. In October 2006, an additional Lehigh Valley mall, The Promenade Shops at Saucon Valley. located off Route 309 in Upper Saucon Township within the Lehigh Valley opened. The Promenade is roughly half the size of the Lehigh Valley Mall but features higher end stores not available in Lehigh Valley Mall. In 2011, The Outlets at Wind Creek Bethlehem opened at Wind Creek Bethlehem in Bethlehem, becoming the first outlet mall in the Lehigh Valley.[61]
Yocco's Hot Dogs, the regionally-famous fast food establishment founded in 1922 and known for their hot dogs and cheesesteaks, maintains four Lehigh Valley locations, including two in Allentown, one in Fogelsville, and one in Trexlertown.
Media
Television
The Lehigh Valley is part of the Philadelphia television market, the nation's fourth largest television market, and also receives television stations from the New York City and Scranton/Wilkes Barre television markets. Lehigh Valley-based stations include WBPH-TV (a Christian television licensed to Bethlehem with studios in Allentown), WFMZ-TV (an independent commercial television station atop South Mountain in Allentown), and WLVT-TV (the PBS station licensed to Allentown with studios in Bethlehem).
Radio
The Lehigh Valley is home to over 35 radio stations, including both English and Spanish-language stations and a range of formats, including all-news, sports radio, talk radio, and NPR. Lehigh Valley station music formats include Top 40, hip hop, rhythmic, country, oldies, polka, soft rock, classic rock, hard rock, and several campus radio stations.
Newspapers
Lehigh Valley-based daily newspapers include The Morning Call and The Express-Times, both of which have been media sources in the Lehigh Valley dating back to the mid-1800s. Two magazines cover the region: Lehigh Valley Style is a regional lifestyle publication based in Easton. Lehigh Valley Magazine, based in Harrisburg, is the region's oldest lifestyle publication.
Film
Multiple movies have been fully or partially filmed in the Lehigh Valley, including M. Night Shyamalan's Glass in 2019, indie dark-comedy Getting Grace starring Daniel Roebuck, Taylor A. Purdee's folk rock musical Killian & the Comeback Kids, and others.[62]
Educationedit
Colleges and universitiesedit
Seven colleges and universities are based in the Lehigh Valley:
- Cedar Crest College (in Allentown)
- DeSales University (in Center Valley)
- Lafayette College (in Easton)
- Lehigh University (in Bethlehem)
- Moravian University (in Bethlehem)
- Muhlenberg College (in Allentown)
- Penn State Lehigh Valley (in Center Valley)
The Lehigh Valley has two two-year colleges:
- Lehigh Carbon Community College (with campuses in Allentown, Carbon County and Schnecksville)
- Northampton Community College (with campuses in Bethlehem, Bethlehem Township and Monroe County)
High school educationedit
The Lehigh Valley is the third most populous metropolitan region in Pennsylvania and served by multiple large school districts, public and private high schools, middle schools, and elementary schools, including:
The largest high schools in the Lehigh Valley and The Poconos (18 in all) compete athletically in the Eastern Pennsylvania Conference. Smaller Lehigh Valley high schools compete in the Colonial League.
Sportsedit




| Club | League | Sport | Venue | Established | Championships |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lehigh Valley IronPigs | IL | Baseball | Coca-Cola Park | 2008 | 0 |
| Lehigh Valley Phantoms | AHL | Ice hockey | PPL Center | 1996 | 2 1997-98 and 2004-05 |
| Lehigh Valley Roller Derby | WFTDA | Roller Derby | Bethlehem Municipal Ice Rink | 2006 | 0 |
| Lehigh Valley United | USL League Two | Soccer | Rocco Calvo Field | 2009 | 1 2012 (conference) |
Footballedit
Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=Lehigh_Valley>Text je dostupný pod licencí Creative Commons Uveďte autora – Zachovejte licenci, případně za dalších podmínek. Podrobnosti naleznete na stránce Podmínky užití.
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok.
Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky
použitia.













