A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
This article needs additional citations for verification. (February 2014) |
In physical geography, a steppe (⫽stɛp⫽) is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without closed forests except near rivers and lakes.[1] Steppe biomes may include:
- the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
- the tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome
- the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome
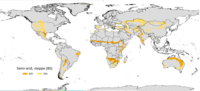
A steppe is usually covered with grass and shrubs, depending on the season and latitude. The term steppe climate denotes a semi-arid climate, which is encountered in regions too dry to support a forest, but not dry enough to be a desert.
Steppes are usually characterized by a semi-arid or continental[citation needed] climate. Extremes can be recorded in the summer of up to 45 °C (115 °F) and in winter of down to −55 °C (−65 °F). Besides this major seasonal difference, fluctuations between day and night are also significant. In both the highlands of Mongolia and northern Nevada, 30 °C (85 °F) can be reached during the day with sub-freezing readings at night.
Steppes average 250–500 mm (10–20 in) of annual precipitation and feature hot summers and cold winters when located in mid-latitudes. In addition to the precipitation level, its combination with potential evapotranspiration defines a steppe climate.
Classification
Steppe can be classified by climate:[2]
- Temperate steppe: the true steppe, found in continental climates[failed verification] can be further subdivided, as in the Rocky Mountains Steppes[2]
- Subtropical steppe: a similar association of plants occurring in the driest areas with a Mediterranean climate[failed verification]; it usually has a short wet period
It can also be classified by vegetation type, e.g. shrub-steppe and alpine-steppe.
Cold steppe
The world's largest steppe region, often referred to as "the Great Steppe", is found in Eastern Europe and Central Asia, and neighbouring countries stretching from Ukraine in the west through Russia, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan to the Altai, Koppet Dag and Tian Shan ranges in China. The Eurasian Steppe is speculated by David W. Anthony to have had a role in the spread of the horse, the wheel and Indo-European languages.[3] In the Eurasian steppe, soils often consist of chernozem.
The inner parts of Anatolia in Turkey, Central Anatolia and East Anatolia in particular and also some parts of Southeast Anatolia, as well as much of Armenia and Iran are largely dominated by cold steppe.
The Pannonian Plain is another steppe region in Central Europe, centered in Hungary but also including portions of Slovakia, Poland, Ukraine, Romania, Serbia, Croatia, Slovenia, and Austria. Another large steppe area (prairie) is located in the central United States, western Canada and the northern part of Mexico. The shortgrass prairie steppe is the westernmost part of the Great Plains region. The Columbia Plateau in southern British Columbia, Oregon, Idaho, and Washington state, is an example of a steppe region in North America outside of the Great Plains.
In South America, cold steppe can be found in Patagonia and much of the high elevation regions east of the southern Andes.
Relatively small steppe areas can be found in the interior of the South Island of New Zealand.
In Australia, a moderately sized temperate steppe region exists in the northern and northwest regions of Victoria, extending to the southern and mid regions of New South Wales. This area borders the semi-arid and arid Australian Outback which is found farther inland on the continent.
Subtropical steppe
In Europe, some Mediterranean areas have a steppe-like vegetation, such as central Sicily in Italy, southern Portugal, parts of Greece in the southern Athens area,[4] and central-eastern Spain, especially the southeastern coast (around Murcia), and places cut off from adequate moisture due to rain shadow effects such as Zaragoza.
In northern Africa, the Mediterranean area also hosts the same steppe-like vegetation, such as the Algerian-Moroccan Hautes Plaines and by extension the North Saharan steppe and woodlands.
In Asia, a subtropical steppe can be found in semi-arid lands that fringe the Thar Desert of the Indian subcontinent as well as much of the Deccan Plateau in the rain shadow of the Western Ghats, and the Badia of the Levant.
In Australia, subtropical steppe can be found in a belt surrounding the most severe deserts of the continent and around the Musgrave Ranges.
In North America this environment is typical of transition areas between zones with a Mediterranean climate and true deserts, such as Reno, Nevada, the inner part of California, and much of western Texas and adjacent areas in Mexico.
-
Steppe in Mongolia
-
Steppe in Kazakhstan
-
Steppe in Turkey
-
Steppe in Russia
-
Steppe in Hungary
-
Steppe in Kherson, Ukraine
-
Southern Siberian steppe: windbreaker trees in the wintertime
-
Cold Patagonian steppe near Fitz Roy, Argentina
-
A guanaco in the Patagonian steppe near Torres del Paine, Chile
-
Prairie in Alberta, Canada
-
Steppe in West Texas
See also
References
- ^
Compare:
Chibilyov, Alexander (2002). "Steppe and Forest-steppe". In Shahgedanova, Maria (ed.). The Physical Geography of Northern Eurasia. Oxford regional environments. Vol. 3 (reprint ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press (published 2003). p. 248. ISBN 978-0-19-823384-8. Retrieved 30 January 2020.
There are many definitions of steppes. For example, Allan (1946) provides fifty-four definitions of this term. Stamp and Clark (1979) define steppes as 'mid-latitude areas dominated by herbaceous vegetation and termed locally steppes, prairies, pampas, high veldts, downland, etc.'
- ^ a b "Ecoregions of the United States-Ecological Subregions of the United States". fs.usda.gov. U.S. Forest Service, U.S. Department of Agriculture. Retrieved 25 October 2016.
- ^ Anthony, David W. (15 August 2010) . The Horse, the Wheel, and Language: How Bronze-Age Riders from the Eurasian Steppes Shaped the Modern World (reprint ed.). Princeton: Princeton University Press (published 2010). p. 240. ISBN 978-0-691-14818-2. Retrieved 12 June 2022.
the critical era when innovative Proto-Indo-European dialects began to spread across the steppes.
- ^ "Hellinikon". HNMS.gr. Greece: Hellenic National Meteorological Service. Archived from the original on 2007-03-12. Retrieved 2013-09-08.
Sources
- Ecology and Conservation of Steppe-land Birds by Manuel B.Morales, Santi Mañosa, Jordi Camprodón, Gerard Bota. International Symposium on Ecology and Conservation of steppe-land birds. Lleida, Spain. December 2004.ISBN 978-84-87334-99-3
External links
- "The Steppes". barramedasoft.com.ar. 1998–2008. Retrieved 2008-04-04.
>Text je dostupný pod licencí Creative Commons Uveďte autora – Zachovejte licenci, případně za dalších podmínek. Podrobnosti naleznete na stránce Podmínky užití.
File:Question book-new.svg
Wikipedia:Verifiability
Special:EditPage/Steppe
Help:Referencing for beginners
Help:Maintenance template removal
steppe
File:BS climate.png
BSk
BSh
File:Eurasian steppe belt.jpg
Great Eurasian Steppe
Eurasia
Physical geography
Help:IPA/English
Ecoregion
Grassland
Plain
Forest
Biome
Montane grasslands and shrublands
Tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands
Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands
Poaceae
Shrub
Season
Latitude
Semi-arid climate
Forest
Desert
Continental climate
Wikipedia:Citation needed
Mongolia
Nevada
Precipitation (meteorology)
Evapotranspiration#Potential evapotranspiration
Humid continental climate#Vegetation
Wikipedia:Verifiability
Rocky Mountains
Mediterranean climate
Wikipedia:Verifiability
Shrub-steppe
Alpine-steppe
Great Steppe
Eastern Europe
Central Asia
Ukraine
Russia
Kazakhstan
Turkmenistan
Uzbekistan
Altay Mountains
Koppet Dag
Tian Shan
China
The Horse, the Wheel and Language
David W. Anthony
Indo-European languages
Soil
Chernozem
Anatolia
Turkey
Central Anatolia
East Anatolia
Southeast Anatolia
Armenia
Iran
Pannonian Plain
Central Europe
Hungary
Slovakia
Poland
Ukraine
Romania
Serbia
Croatia
Slovenia
Austria
Prairie
United States
Western Canada
Mexico
Shortgrass prairie
Great Plains
Columbia Plateau (ecoregion)
British Columbia
Oregon
Idaho
Washington (state)
North America
South America
Patagonia
Andes
South Island
New Zealand
Australia
Victoria (Australia)
New South Wales
Outback
Europe
Mediterranean climate
Sicily
Italy
Portugal
Greece
Athens
Spain
Murcia
Rain shadow
Zaragoza
Africa
Mediterranean climate
Hautes Plaines
North Saharan steppe and woodlands
Asia
Thar Desert
Indian subcontinent
Deccan Plateau
Western Ghats
Badia (region)
Levant
Australia
Musgrave Ranges
North America
Reno, Nevada
California
West Texas
File:Naadam rider 2.jpg
Mongolia
File:Steppe of western Kazakhstan in the early spring.jpg
Kazakhstan
File:HASAN DAĞI - panoramio.jpg
Turkey
File:Чубовская степь.JPG
Russia
File:Hortobágy.jpg
Hungary
File:Typical agricultural landscape of Kherson Oblast.jpg
Kherson Oblast
File:Windbreakers altai steppe.jpg
Siberia
Windbreak
File:Patagonian plains argentina.jpg
Patagonia
Fitz Roy
File:Guanaco Patagonico.jpg
Torres del Paine
File:Prairie Alberta.jpg
Alberta
File:2013-07-04 15 37 14 Sagebrush-steppe along U.S. Route 93 in central Elko County in Nevada.jpg
Sagebrush steppe
Nevada
U.S. Route 93 in Nevada
File:West Texas Hwy 302 west of NoTrees.jpg
West Texas
Grassland
Plain
Prairie
Tugay
Tundra
ISBN (identifier)
Special:BookSources/978-0-19-823384-8
U.S. Forest Service
U.S. Department of Agriculture
David W. Anthony
ISBN (identifier)
Special:BookSources/978-0-691-14818-2
ISBN (identifier)
Special:BookSources/978-84-87334-99-3
Category:Steppes
Template:Vegetation
Template talk:Vegetation
Special:EditPage/Template:Vegetation
Phytogeography
Vegetation classification
Forest
Woodland
Arboretum
Shrubland
Heath
Thicket
Dwarf-shrub
Subshrub
Herbaceous
Grassland
Prairie
Savanna
Aspen parkland
Desert vegetation
Desert
Barren vegetation
Tropical
Subtropical
Temperate
Subarctic climate
Polar climate
Pluvial
Rainforest
Cloud forest
Seasonal
Drought
Montane
Submontane
Lowland
Coastal
Deciduous
Semi-deciduous
Evergreen
Sclerophyll
Broad-leaved
Terrestrial vegetation
Aquatic vegetation
Riparian
Mangrove
Swamp
Biogeographic realm
Biome
Floristic kingdom
Plant habit
Plant life-form
Vegetation
Template:Earth's landforms
Template talk:Earth's landforms
Special:EditPage/Template:Earth's landforms
Earth
Landform
Glossary of landforms
Butte
Hill
Flat (landform)
Mountain
Mountain range
Plateau
Ridge
Table (landform)
Valley
Ice sheet
Plain
Tundra
Fluvial processes
Alluvial fan
Beach
Canyon
Cave
Channel (geography)
Cliff
Lake
Lake island
Levee
Floodplain
Meander
Oasis
Pond
Rapids
River
River delta
River mouth
Strait
Swamp
Valley
Waterfall
Glacial landform
Arête
Cirque
Esker
Glacier
Ice field
Fjord
Tunnel valley
Coastal geography
Atoll
Bay
Cape (geography)
Channel (geography)
Coast
Continental shelf
Coral reef
Estuary
Island
Isthmus
Lagoon
Mid-ocean ridge
Oceanic trench
Peninsula
Seamount
Volcanic island
Caldera
Geyser
Guyot
Lava dome
Lava field
Mid-ocean ridge
Submarine volcano
Volcanic crater
Volcanic crater lake
Volcanic dam
Volcanic island
Volcanic plateau
Volcanic plug
Volcano
Wall rock
Aeolian processes
Desert
Dry lake
Dune
Sandhill
Tundra
Artificial island
Artificial reef
Bridge
Building
Canal
Dam
Ditch
Land reclamation
Levee
Polder
Quarry
Reservoir
Updating...x
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok.
Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky
použitia.