A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
A trauma center, or trauma centre, is a hospital equipped and staffed to provide care for patients suffering from major traumatic injuries such as falls, motor vehicle collisions, or gunshot wounds. A trauma center may also refer to an emergency department (also known as a "casualty department" or "accident and emergency") without the presence of specialized services to care for victims of major trauma.
In the United States, a hospital can receive trauma center status by meeting specific criteria established by the American College of Surgeons (ACS) and passing a site review by the Verification Review Committee.[1] Official designation as a trauma center is determined by individual state law provisions. Trauma centers vary in their specific capabilities and are identified by "Level" designation, Level I (Level-1) being the highest and Level III (Level-3) being the lowest (some states have four or five designated levels).
The highest levels of trauma centers have access to specialist medical and nursing care, including emergency medicine, trauma surgery, critical care, neurosurgery, orthopedic surgery, anesthesiology, and radiology, as well as a wide variety of highly specialized and sophisticated surgical and diagnostic equipment.[2][3][4] Lower levels of trauma centers may be able to provide only initial care and stabilization of a traumatic injury and arrange for transfer of the patient to a higher level of trauma care.
The operation of a trauma center is often expensive and some areas may be underserved by trauma centers because of that expense.[citation needed] As there is no way to schedule the need for emergency services, patient traffic at trauma centers can vary widely.[citation needed]
A trauma center may have a helipad for receiving patients that have been airlifted to the hospital. In some cases, persons injured in remote areas and transported to a distant trauma center by helicopter can receive faster and better medical care than if they had been transported by ground ambulance to a closer hospital that does not have a designated trauma center.
History
United Kingdom

Trauma centres grew into existence out of the realisation that traumatic injury is a disease process unto itself requiring specialised and experienced multidisciplinary treatment and specialised resources. The world's first trauma centre, the first hospital to be established specifically to treat injured rather than ill patients, was the Birmingham Accident Hospital, which opened in Birmingham, England in 1941 after a series of studies found that the treatment of injured persons within England was inadequate. By 1947, the hospital had three trauma teams, each including two surgeons and an anaesthetist, and a burns team with three surgeons. The hospital became part of the National Health Service in its formation in July 1948 and closed in 1993.[5] The NHS now has 27 major trauma centres established across England, four in Scotland, and one planned in Wales.
United States



According to the CDC, injuries are the leading cause of death for American children and young adults ages 1–19.[6] The leading causes of trauma are motor vehicle collisions, falls, and assaults with a deadly weapon.
In the United States, Robert J. Baker and Robert J. Freeark established the first civilian Shock Trauma Unit at Cook County Hospital in Chicago, Illinois on March 16, 1966.[7] The concept of a shock trauma center was also developed at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, in the 1950s and 1960s by thoracic surgeon and shock researcher R Adams Cowley, who founded what became the Shock Trauma Center in Baltimore, Maryland, on July 1, 1966. The R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center is one of the first shock trauma centers in the world.[8] Cook County Hospital in Chicago trauma center (opened in 1966).[9] David R. Boyd interned at Cook County Hospital from 1963 to 1964 before being drafted into the Army of the United States of America. Upon his release from the Army, Boyd became the first shock-trauma fellow at the R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center, and then went on to develop the National System for Emergency Medical Services, under President Ford.[10] In 1968 the American Trauma Society was created by various co-founders, including R Adams Cowley and Rene Joyeuse as they saw the importance of increased education and training of emergency providers and for nationwide quality trauma care.
Canada
According to the founder of the Trauma Unit at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre in Toronto, Ontario, Marvin Tile, "the nature of injuries at Sunnybrook has changed over the years. When the trauma centre first opened in 1976, about 98 per cent of patients suffered from blunt-force trauma caused by accidents and falls. Now, as many as 20 per cent of patients arrive with gunshot and knife wounds".[11]
Fraser Health Authority in British Columbia, located at Royal Columbian Hospital and Abbotsford Regional Hospital, services the BC area, "Each year, Fraser Health treats almost 130,000 trauma patients as part of the integrated B.C. trauma system".[12]
Definitions in United States
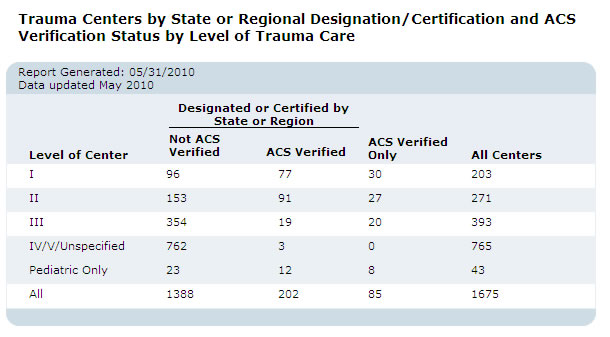
In the United States, trauma centers are ranked by the American College of Surgeons (ACS) or local state governments, from Level I (comprehensive service) to Level III (limited-care). The different levels refer to the types of resources available in a trauma center and the number of patients admitted yearly. These are categories that define national standards for trauma care in hospitals. Level I and Level II designations are also given adult or pediatric designations.[13] Additionally, some states have their own trauma-center rankings separate from the ACS. These levels may range from Level I to Level IV. Some hospitals are less-formally designated Level V.
The ACS does not officially designate hospitals as trauma centers. Numerous U.S. hospitals that are not verified by ACS claim trauma center designation. Most states have legislation that determines the process for designation of trauma centers within that state. The ACS describes this responsibility as "a geopolitical process by which empowered entities, government or otherwise, are authorized to designate." The ACS's self-appointed mission is limited to confirming and reporting on any given hospital's ability to comply with the ACS standard of care known as Resources for Optimal Care of the Injured Patient.[14]
The Trauma Information Exchange Program (TIEP)[15] is a program of the American Trauma Society in collaboration with the Johns Hopkins Center for Injury Research and Policy and is funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. TIEP maintains an inventory of trauma centers in the US, collects data and develops information related to the causes, treatment and outcomes of injury, and facilitates the exchange of information among trauma care institutions, care providers, researchers, payers and policymakers.[citation needed]
A trauma center is a hospital that is designated by a state or local authority or is verified by the American College of Surgeons.[16]
Level I
A Level I trauma center provides the highest level of surgical care to trauma patients. Being treated at a Level I trauma center can reduce mortality by 25% compared to a non-trauma center.[17] It has a full range of specialists and equipment available 24 hours a day[18] and admits a minimum required annual volume of severely injured patients.
A Level I trauma center is required to have a certain number of the following people on duty 24 hours a day at the hospital:
- surgeons
- emergency physicians
- anesthesiologists
- nurses
- respiratory therapists
- an education program
- preventive and outreach programs.
Key elements include 24‑hour in‑house coverage by general surgeons and prompt availability of care in varying specialties—such as orthopedic surgery, cardiothoracic surgery, neurosurgery, plastic surgery, anesthesiology, emergency medicine, radiology, internal medicine, otolaryngology, oral and maxillofacial surgery, and critical care, which are needed to adequately respond and care for various forms of trauma that a patient may suffer, as well as provide rehabilitation services.[citation needed]
Most Level I trauma centers are teaching hospitals/campuses. Additionally, a Level I center has a program of research, is a leader in trauma education and injury prevention, and is a referral resource for communities in nearby regions.[19]
Level II
A Level II trauma center works in collaboration with a Level I center. It provides comprehensive trauma care and supplements the clinical expertise of a Level I institution. It provides 24-hour availability of all essential specialties, personnel, and equipment. Oftentimes, level II centers possess critical care services capable of caring for almost all injury types indefinitely. Minimum volume requirements may depend on local conditions. Such institutions are not required to have an ongoing program of research or a surgical residency program.[citation needed]
Level III
A Level III trauma center does not have the full availability of specialists but has resources for emergency resuscitation, surgery, and intensive care of most trauma patients. A Level III center has transfer agreements with Level I or Level II trauma centers that provide back-up resources for the care of patients with exceptionally severe injuries, such as multiple trauma.[19]
Level IV
A Level IV trauma center exists in some states in which the resources do not exist for a Level III trauma center. It provides initial evaluation, stabilization, diagnostic capabilities, and transfer to a higher level of care. It may also provide surgery and critical-care services, as defined in the scope of services for trauma care. A trauma-trained nurse is immediately available, and physicians are available upon the patient's arrival in the Emergency Department. Transfer agreements exist with other trauma centers of higher levels, for use when conditions warrant a transfer.[19][20]
Level V
A Level V trauma center provides initial evaluation, stabilization, diagnostic capabilities, and transfer to a higher level of care. They may provide surgical and critical-care services, as defined in the service's scope of trauma care services. A trauma-trained nurse is immediately available, and physicians are available upon patient arrival in the emergency department. If not open 24 hours daily, the facility must have an after-hours trauma response protocol.[citation needed]
Pediatric trauma centers
A facility can be designated an adult trauma center, a pediatric trauma center, or an adult and pediatric trauma center. If a hospital provides trauma care to both adult and pediatric patients, the level designation may not be the same for each group. For example, a Level I adult trauma center may also be a Level II pediatric trauma center because pediatric trauma surgery is a specialty unto itself. Adult trauma surgeons are not generally specialized in providing surgical trauma care to children and vice versa, and the difference in practice is significant. In contrast to adult trauma centers, pediatric trauma centers only have two ratings, either level I or level II.[citation needed]
See also
- List of trauma centers in the United States
- Emergency medicine
- Trauma (medicine)
- Trauma surgery
- Trauma team
- Traumatology
References
- ^ "Verification, Review, and Consultation Program for Hospitals". facs.org. Retrieved 2017-11-23.
- ^ Andrew B., MD Peitzman; Andrew B. Peitzman; Michael, MD Sabom; Donald M., MD Yearly; Timothy C., MD Fabian (2002). The Trauma Manual. Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 3. ISBN 0-7817-2641-7.
- ^ "Consultation/Verification Program Reference Guide of Suggested Classification" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on April 1, 2013.
- ^ American College of Surgeons (2006). Consultation/Verification Program, Reference Guide of Suggested Classification. American College of Surgeons. p. 3. ISBN 0-7817-2641-7.
- ^ Wilson, William C. (2007). "History of Trauma". Trauma: Emergency Resuscitation, Perioperative Anesthesia, Surgical Management. Vol. 1. New York: CRC Press. p. 18. ISBN 978-0824729196. Retrieved 2012-05-17.
- ^ "Accident Statistics". Stanford Children's health. 19 April 2020.
- ^ Medical World News, January 27, 1967
- ^ "R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center History". University of Maryland Medical Center. 27 March 2008.
- ^ "Old Cook County Hospital page". Cook County Hospital. Archived from the original on 2009-02-27.
- ^ "National Safety Council Presents David R. Boyd, MDCM, FACS, With Service to Safety Award". American College of Surgeons. Archived from the original on 2011-07-21.
- ^ "Sunnybrook doctor names to Order of Canada", Community July 8, 2009 City Centre Mirror
- ^ Fraser Health regional trauma program receives distinction award, media@fraserhealth.ca, July 5, 2016
- ^ "ACS Verification Site Visit Outcomes". facs.org. Retrieved 2017-11-23.
- ^ "About the VRC Program". American College of Surgeons.
- ^ Trauma Information Exchange Program Archived 2012-08-05 at the Wayback Machine, American Trauma Society
- ^ Trauma Center Designation and Verification by Level of Trauma Care, Trauma Information Exchange Program, American Trauma Society
- ^ Faul, Mark; Sasser, Scott M.; Lairet, Julio; Mould-Millman, Nee-Kofi; Sugerman, David (2015). "Trauma Center Staffing, Infrastructure, and Patient Characteristics that Influence Trauma Center Need". Western Journal of Emergency Medicine. 16 (1): 98–106. doi:10.5811/westjem.2014.10.22837. ISSN 1936-900X. PMC 4307735. PMID 25671017.
- ^ Ackerman, Todd (2011-03-25). "UTMB trauma center Level 1 again". Houston Chronicle. Retrieved 2011-03-26.
- ^ a b c Public Relations. "Trauma & Critical Care Center-Trauma Center levels". Khon Kaen Regional Hospital (in Thai). Thailand: Department of Hospital Health. Archived from the original on 2003-07-21.
- ^ "Emergency Trauma Center". Pioneers Medical Center. Meeker, Colorado. Archived from the original on 2013-10-31. Retrieved 2014-12-29.
External links
- Current listing of Verified Trauma Centers in the United States—American College of Surgeons
- Verified Trauma Center Program—American College of Surgeons
- Find your nearest A&E (accident and emergency)—United Kingdom National Health Service
- Injury Prevention & Control: Trauma Care at Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Trauma Centers Fact Sheet at Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Trauma Levels Explained, American Trauma Society
- Trauma Center Association of America, formerly known as the National Foundation for Trauma Care
- U.S. Trauma Center Crisis Report (2004)
- Report: U.S. Trauma Center Preparedness for a Terrorist Attack in the Community
- Report: Harris Poll: Trauma Care: Public's Knowledge and Perception of Importance 2004
- NHS England major trauma centres
- NHS England 2012 major trauma centres map Urgent and emergency care services
- NHS England Ambulance trauma coding When to call 999
- NHS Wales trauma centres Accident and emergency departments
- NHS Scotland trauma centres list
State trauma system regulation
- Bureau of Emergency Medical Services & Trauma System, Arizona Department of Health Services
- Arizona Trauma Center Designation
- Arizona Trauma System
- Georgia Trauma Commission
- PA Trauma Systems Foundation
- 25 Texas Administrative Code 157.125 (Texas Requirements for Trauma Facility Designation)
- Maryland Trauma System
>Text je dostupný pod licencí Creative Commons Uveďte autora – Zachovejte licenci, případně za dalších podmínek. Podrobnosti naleznete na stránce Podmínky užití.
Hospital
Major trauma
Falling (accident)
Motor vehicle collision
Gunshot wound
Emergency department
Major trauma
American College of Surgeons
Nurse
Emergency medicine
Trauma surgery
Critical care medicine
Neurosurgery
Orthopedic surgery
Anesthesiology
Radiology
Wikipedia:Citation needed
Wikipedia:Citation needed
Helipad
Air medical services
Helicopter
Ambulance
File:Birmingham Accident Hospital R.jpg
Birmingham Accident Hospital
Birmingham
Major trauma
Birmingham Accident Hospital
Birmingham
Trauma team
National Health Service (England)
Major Trauma Centre
NHS England
NHS Scotland
NHS Wales
List of trauma centers in the United States
File:OSU Wexner Medical Center campus 01.jpg
Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center
Columbus, Ohio
File:MemorialHermannMedCentHoustonTX2009.JPG
Memorial Hermann–Texas Medical Center
Houston
File:Aerial-Picture-of-Jackson-e1445995779731.jpg
Jackson Memorial Hospital
Miami
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
University of Maryland, Baltimore
Shock (circulatory)
R Adams Cowley
Shock Trauma Center
Baltimore
Maryland
Cook County Hospital
Cook County Hospital
United States Army
Emergency medical services
Gerald Ford
R Adams Cowley
Rene Joyeuse
Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre
Toronto
Marvin Tile
Knife
Fraser Health Authority
British Columbia
Royal Columbian Hospital
List of trauma centers in the United States
American College of Surgeons
Hospital
Pediatric
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Wikipedia:Citation needed
File:Traumaccenters.jpg
Physical trauma
Surgery
Emergency physician
Anesthesiologist
Nursing
Respiratory Therapist
Orthopedic surgery
Cardiothoracic surgery
Neurosurgery
Plastic surgery
Anesthesiology
Emergency medicine
Radiology
Internal medicine
Otolaryngology
Oral and maxillofacial surgery
Intensive-care medicine
Wikipedia:Citation needed
Wikipedia:Citation needed
Wikipedia:Citation needed
Wikipedia:Citation needed
File:P parthenon.svg
Portal:Architecture
Portal:Medicine
List of trauma centers in the United States
Emergency medicine
Trauma (medicine)
Trauma surgery
Trauma team
Traumatology
ISBN (identifier)
Special:BookSources/0-7817-2641-7
ISBN (identifier)
Special:BookSources/0-7817-2641-7
ISBN (identifier)
Special:BookSources/978-0824729196
Wayback Machine
Doi (identifier)
ISSN (identifier)
PMC (identifier)
PMID (identifier)
Houston Chronicle
Template:Emergency medicine
Template talk:Emergency medicine
Special:EditPage/Template:Emergency medicine
Emergency medicine
Emergency department
Emergency medical services
Emergency nursing
Emergency psychiatry
Golden hour (medicine)
Medical emergency
International emergency medicine
Pediatric emergency medicine
Pre-hospital emergency medicine
Major trauma
Triage
Category:Emergency medical equipment
Bag valve mask
Chest tube
Defibrillation
Automated external defibrillator
Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
Electrocardiography
Intraosseous infusion
Intravenous therapy
Tracheal intubation
Laryngeal tube
Combitube
Nasopharyngeal airway
Oropharyngeal airway
Pocket mask
Adenosine
Amiodarone
Atropine
Dopamine
Epinephrine
Naloxone
Magnesium sulfate
Sodium bicarbonate
Category:Emergency medicine organisations
International Federation for Emergency Medicine
International Conference on Emergency Medicine
American College of Emergency Physicians
Australasian College for Emergency Medicine
Canadian Association of Emergency Physicians
Royal College of Emergency Medicine
European Society for Emergency Medicine
Asian Society for Emergency Medicine
American Academy of Emergency Medicine
Category:Emergency medicine courses
Category:Emergency life support
First aid
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
Mouth-to-mouth resuscitation
Basic life support
Advanced cardiac life support
Advanced trauma life support
Neonatal Resuscitation Program
Acute Care of at-Risk Newborns
Pediatric basic life support
Pediatric Advanced Life Support
Advanced Life Support in Obstetrics
Care of the Critically Ill Surgical Patient
NACA score
Injury Severity Score
Category:Emergency medicine
Outline of emergency medicine
Template:Trauma
Template talk:Trauma
Special:EditPage/Template:Trauma
Injury
Polytrauma
Major trauma
Traumatology
Triage
Resuscitation
Trauma triad of death
Clinical prediction rule
Abbreviated Injury Scale
Injury Severity Score
NACA score
Revised Trauma Score
Diagnostic peritoneal lavage
Focused assessment with sonography for trauma
Advanced trauma life support
Damage control surgery
Early appropriate care
Trauma surgery
Trauma team
Resuscitative thoracotomy
Injury
Bone fracture
Degloving
Joint dislocation
Soft tissue injury
Diaphragmatic rupture
Flail chest
Hemothorax
Pneumothorax
Pulmonary contusion
Cardiac tamponade
Internal bleeding
Thoracic aorta injury
Blunt kidney trauma
Splenic injury
Intracranial hemorrhage
Penetrating head injury
Traumatic brain injury
Blast injury
Blunt trauma
Burn
Crush injury
Electrocution
Gunshot wound
Penetrating trauma
Stab wound
Abdominal trauma
Chest injury
Facial trauma
Head injury
Spinal cord injury
Geriatric trauma
Trauma in children
Acute respiratory distress syndrome
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy
Compartment syndrome
Contracture
Volkmann's contracture
Crush syndrome
Rhabdomyolysis
Embolism
Air embolism
Fat embolism syndrome
Post-traumatic stress disorder
Subcutaneous emphysema
Wound healing
Template:Hospital articles
Template talk:Hospital articles
Special:EditPage/Template:Hospital articles
Hospital
History of hospitals
Hospital network
Category:Hospitals
Hospital accreditation
Hospital bed
Coronary care unit
Emergency department
Hospital emergency codes
Health administration#Hospital administrators
Hospital information system
Hospital medicine
Hospital museum
Hospital medicine
Intensive care unit
Nocturnist
On-call room
Operating theater
Orderly
Patients#Outpatients and inpatients
Hospital pharmacy
Hospital ward
Almshouse
Asclepeion
Bimaristan
Cottage hospital
Medical community of ancient Rome#Imperial
Vaishya
Xenodochium
Base hospital
Community hospital
General hospital
Regional hospital
District hospital
Municipal hospital
Day hospital
Secondary hospital
Tertiary referral hospital
Teaching hospital
Specialty hospital
Hospital ship
Hospital train
Mobile hospital
Underground hospital
Virtual Hospital
Military hospital
Combat support hospital
Field hospital
Category:Prison hospitals
List of Veterans Affairs medical facilities
Category:Women's hospitals
Charitable hospital
For-profit hospital
Non-profit hospital
State hospital
Private hospital
Public hospital
Voluntary hospital
Category:Defunct hospitals
Category:Cancer hospitals
Children's hospital
Category:Eye hospitals
Fever hospital
Leper colony
Lock hospital
Maternity hospital
Updating...x
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok.
Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky
použitia.