A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2023) |
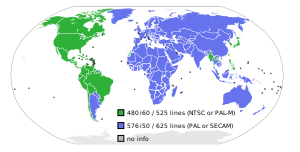
480i is the video mode used for standard-definition digital video[1] in the Caribbean, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, Philippines, Myanmar, Western Sahara, and most of the Americas (with the exception of Argentina, Paraguay, and Uruguay). The other common standard definition digital standard, used in the rest of the world, is 576i.
It originated from the need for a standard to digitize analog TV (defined in BT.601) and is now used for digital TV broadcasts and home appliances such as game consoles and DVD disc players.[1][2]
The 480 identifies a vertical resolution of 480 lines, and the i identifies it as an interlaced resolution. The field rate, which is 60 Hz (or 59.94 Hz when used with NTSC color), is sometimes included when identifying the video mode, i.e. 480i60; another notation, endorsed by both the International Telecommunication Union in BT.601[3] and SMPTE in SMPTE 259M, includes the frame rate, as in 480i/30.
Although related, it should not be confused with the analog "525 lines" resolution, mandated by CCIR Systems M and J and usually paired with NTSC color. This association explains why 480i is sometimes inaccurately called "NTSC", even though NTSC only exists in the analog domain.
Technical details

For analog NTSC, there are a total of 525 scanning lines per frame of which originally 483 lines were visible (241.5 visible lines per field + 21 lines of vertical blanking per field = 483 + 42 = 525 lines per frame) and later 480 (240 complete lines per field).
A full frame consists of two fields. One field contains the odd-numbered lines and the other contains the even ones. By convention an NTSC video frame is considered to start with an even field followed by an odd field. The disparity of the line numbering compared to other systems is solved by defining the line numbering to start five equalizing pulses (or 2 and a half lines) earlier than on all other systems, including Systems A (405-line) and E (819-line) even though they had no equalizing pulses, on the first equalizing pulse following an active line or half line. This has the effect of placing a half line of video at the end of the even (first) field and the beginning of the odd (second field). Thus the line numbers correspond to the real lines of the video frame. On all other systems, the field was considered to start with the falling edge of the first field pulse which gave the confusing position that the odd field (first) had a half a line of video occupying the latter half of a whole line and ended with a whole line of video but half a scanning line (and vice versa for the even field). The NTSC convention solved this confusion.[4]
For DV-NTSC only 480 lines are used. The digitally transmitted horizontal resolution is usually 720 samples (which includes 16 samples for the horizontal sync and horizontal blanking) or 704 visible pixels with an aspect ratio of 4:3 (with vertically rectangular pixels) and therefore a display resolution of 640 × 480 (VGA); that is standard-definition television (SDTV) with a 4:3 aspect ratio (with square pixels).[5][6][7]
The field rate (not the frame rate) is usually (60/1.001) = 59.94 hertz for color TV and is often incorrectly rounded up to 60 Hz. There are several conventions for written shorthands for the combination of resolution and rate: 480i60, 480i/30 (EBU/SMPTE always use frame rate to specify interlaced formats) and 480/60i. 480i is usually used in countries that conventionally use NTSC (most of the Americas and Japan), because the 525 transmitted lines at 60 hertz of analogue NTSC contain 480 visible ones.
In each case of the use of the ‘60’ terminology, it is merely shorthand for 59.94, to differentiate it from 30 (29.97) or 24 (23.976).
Color information is stored using the YCbCr color space (different from NTSC that used YIQ) with 4:2:2 sampling (also different from NTSC) and following Rec. 601 colorimetry.
480i can be transported by all major digital television formats (ATSC, DVB and ISDB) and on DVD.
See also
- Enhanced-definition television (EDTV)
- List of common resolutions
- 4320p, 2160p, 1080p, 1080i, 720p, 576p, 576i, 480p, 360p, 240p
References
- ^ a b "What means 480i? - AfterDawn". www.afterdawn.com.
- ^ "BT.601: Studio encoding parameters of digital television for standard 4:3 and wide screen 16:9 aspect ratios". ITU.
- ^ "Recommendation ITU-R BT.601-7, Studio encoding parameters of digital television for standard 4:3 and wide-screen 16:9 aspect ratios" (PDF). International Telecommunication Union. March 2011.
- ^ Report 308-2 of the XIIth Plenary of the CCIR - Characteristics of TV systems.
- ^ "rpsoft 2000 software". rpsoft2000.com. Retrieved 1 June 2015.
- ^ "480i". afterdawn.com. Retrieved 1 June 2015.
- ^ "Glossary - 480i".
>Text je dostupný pod licencí Creative Commons Uveďte autora – Zachovejte licenci, případně za dalších podmínek. Podrobnosti naleznete na stránce Podmínky užití.
525 lines
File:Question book-new.svg
Wikipedia:Verifiability
Special:EditPage/480i
Help:Referencing for beginners
Help:Maintenance template removal
File:TV-line-count-world.svg
Video
Standard-definition television
Digital video
Caribbean
Japan
South Korea
Taiwan
Philippines
Myanmar
Western Sahara
Americas
Argentina
Paraguay
Uruguay
576i
Rec. 601
Interlaced video
Refresh rate
Hertz
International Telecommunication Union
Rec. 601
SMPTE 259M
Frame rate
525 lines
CCIR System M
NTSC
File:Balayage entrelace affichage trames.svg
Scan line
Vertical blanking interval
CCIR System A
CCIR System E
DV (video format)
Digital television
Pixel
Aspect ratio (image)
Video Graphics Array
Standard-definition television
Refresh rate
Frame rate
Hertz
Television
European Broadcasting Union
Japan
YCbCr
Color space
YIQ
Chroma subsampling#4:2:2
Rec. 601
Digital television
ATSC standards
DVB
ISDB
DVD
File:Blank television set.svg
Portal:Television
Enhanced-definition television
List of common resolutions
8K resolution
4K resolution#2160p resolution
1080p
1080i
720p
576p
576i
480p
Low-definition television
Low-definition television
Template:TV resolution
Template talk:TV resolution
Special:EditPage/Template:TV resolution
Display resolution
MPEG-2
Low-definition television
Video CD
Mobile television
Source Input Format
Low-definition television
Standard-definition television
Super Video CD
DVD
DV (video format)
NTSC
PAL
SECAM
576i
480p
576p
Enhanced-definition television
480p
576p
High-definition television
Blu-ray
HD DVD
HDV
720p
1080i
1080p
Ultra-high-definition television
Ultra HD Blu-ray
Ultra-high-definition television
Template:Video formats
Template talk:Video formats
Special:EditPage/Template:Video formats
Video
Analog television
405-line television system
CCIR System A
525 lines
CCIR System M
NTSC
NTSC-J
Clear-Vision
PAL-M
B-MAC
625 lines
CCIR System B
CCIR System C
CCIR System D
CCIR System G
CCIR System H
CCIR System I
CCIR System K
CCIR System L
CCIR System N
PAL
PAL#PALN
PALplus
SECAM
Multiplexed Analogue Components
819 line
CCIR System E
CCIR System E#System F
Multiple sub-Nyquist sampling encoding
HD-MAC
Audio signal
Multichannel television sound
EIAJ MTS
NICAM
Second audio program
Sound-in-Syncs
Zweikanalton
Closed captioning
CGMS-A
Electronic program guide
Ghost-canceling reference
Programme Delivery Control
Teletext
Vertical blanking interval
Video Encoded Invisible Light
VIT signals
Vertical interval timecode
Widescreen signaling
Extended Data Services
Television systems before 1940
Mechanical television
180-line television system
343-line television system
375-line television system
441-line television system
455-line television system
567-line television system
Field-sequential color system
Soviet Central Television#OSKM
Digital television
Interlaced video
Standard-definition television
576i
High-definition television
1080i
Progressive scan
Low-definition television
1seg
Low-definition television
Low-definition television
Enhanced-definition television
480p
576p
High-definition television
720p
1080p
Ultra-high-definition television
4K resolution
8K resolution
H.262/MPEG-2 Part 2
ATSC standards
DVB
DVB 3D-TV
ISDB
Digital Terrestrial Multimedia Broadcast
ChinaSat 9
Audio Video Standard#First generation
China Multimedia Mobile Broadcasting
Audio Video Standard#First generation
Digital Terrestrial Multimedia Broadcast
ChinaSat 9
MPEG-4 Part 2
MobaHo!
Advanced Video Coding
ATSC standards#H.264/MPEG-4 AVC
China Multimedia Mobile Broadcasting
Digital multimedia broadcasting
Digital Terrestrial Multimedia Broadcast
Digital Video Broadcasting
ISDB-T International
1seg
MobaHo!
Audio Video Standard#Second generation
ChinaSat 9
High Efficiency Video Coding
ATSC 3.0
Digital Video Broadcasting
Digital multimedia broadcasting
ISDB#ISDB-S3
Digital Terrestrial Multimedia Broadcast
Surround sound
Dolby Digital
Surround sound
Dolby AC-4
DTS (sound system)
Dynamic Resolution Adaptation
MPEG-1 Audio Layer II
MPEG Multichannel
Pulse-code modulation
Linear pulse-code modulation
Advanced Audio Coding
High-Efficiency Advanced Audio Coding
MPEG-H 3D Audio
Active Format Description
Broadcast flag
Closed captioning
DVB-CPCM
Electronic program guide
Teletext
14:9
Broadcast-safe
Digital cinema
Digital Cinema Initiative
Display motion blur
Moving image formats
MPEG transport stream
Reverse Standards Conversion
Television standards conversion
Television transmitter
Test card
Video on demand
Video processing
Widescreen signaling
Template:Analogue TV transmitter topics
480i
480i
Main Page
Wikipedia:Contents
Portal:Current events
Special:Random
Wikipedia:About
Wikipedia:Contact us
Special:FundraiserRedirector?utm source=donate&utm medium=sidebar&utm campaign=C13 en.wikipedia.org&uselang=en
Help:Contents
Help:Introduction
Wikipedia:Community portal
Special:RecentChanges
Wikipedia:File upload wizard
Main Page
Special:Search
Help:Introduction
Special:MyContributions
Special:MyTalk
480i
480i
۴۸۰آی
480i
480i
480մ
480आई
480i
480i
480i
480i
480i
480i
480i
480i
480i
480i
480i
480i
480i
480i
Special:EntityPage/Q1195242#sitelinks-wikipedia
480i
Talk:480i
480i
480i
Special:WhatLinksHere/480i
Special:RecentChangesLinked/480i
Wikipedia:File Upload Wizard
Special:SpecialPages
Special:EntityPage/Q1195242
480i
480i
Main Page
Wikipedia:Contents
Portal:Current events
Special:Random
Wikipedia:About
Wikipedia:Contact us
Special:FundraiserRedirector?utm source=donate&utm medium=sidebar&utm campaign=C13 en.wikipedia.org&uselang=en
Help:Contents
Help:Introduction
Wikipedia:Community portal
Special:RecentChanges
Updating...x
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok.
Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky
použitia.

