A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
|
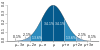
Probability density function  The red curve is the standard normal distribution | |||
|
Cumulative distribution function  | |||
| Notation | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters |
= mean (location) = variance (squared scale) | ||
| Support | |||
| CDF | |||
| Quantile | |||
| Mean | |||
| Median | |||
| Mode | |||
| Variance | |||
| MAD | |||
| Skewness | |||
| Ex. kurtosis | |||
| Entropy | |||
| MGF | |||
| CF | |||
| Fisher information |
| ||
| Kullback-Leibler divergence | |||
| Part of a series on statistics |
| Probability theory |
|---|
 |
In statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is
The parameter is the mean or expectation of the distribution (and also its median and mode), while the parameter is its standard deviation. The variance of the distribution is . A random variable with a Gaussian distribution is said to be normally distributed, and is called a normal deviate.
Normal distributions are important in statistics and are often used in the natural and social sciences to represent real-valued random variables whose distributions are not known.[1][2] Their importance is partly due to the central limit theorem. It states that, under some conditions, the average of many samples (observations) of a random variable with finite mean and variance is itself a random variable—whose distribution converges to a normal distribution as the number of samples increases. Therefore, physical quantities that are expected to be the sum of many independent processes, such as measurement errors, often have distributions that are nearly normal.[3]
Moreover, Gaussian distributions have some unique properties that are valuable in analytic studies. For instance, any linear combination of a fixed collection of normal deviates is a normal deviate. Many results and methods, such as propagation of uncertainty and least squares parameter fitting, can be derived analytically in explicit form when the relevant variables are normally distributed.
A normal distribution is sometimes informally called a bell curve.[4] However, many other distributions are bell-shaped (such as the Cauchy, Student's t, and logistic distributions). For other names, see Naming.
The univariate probability distribution is generalized for vectors in the multivariate normal distribution and for matrices in the matrix normal distribution.
Definitions
Standard normal distribution
The simplest case of a normal distribution is known as the standard normal distribution or unit normal distribution. This is a special case when and , and it is described by this probability density function (or density):
The variable has a mean of 0 and a variance and standard deviation of 1. The density has its peak at and inflection points at and .
Although the density above is most commonly known as the standard normal, a few authors have used that term to describe other versions of the normal distribution. Carl Friedrich Gauss, for example, once defined the standard normal as
which has a variance of 1/2, and Stephen Stigler[5] once defined the standard normal as
which has a simple functional form and a variance of :
General normal distribution
Every normal distribution is a version of the standard normal distribution, whose domain has been stretched by a factor (the standard deviation) and then translated by (the mean value):
The probability density must be scaled by so that the integral is still 1.
If is a standard normal deviate, then will have a normal distribution with expected value and standard deviation . This is equivalent to saying that the "standard" normal distribution can be scaled/stretched by a factor of and shifted by to yield a different normal distribution, called . Conversely, if is a normal deviate with parameters and , then this distribution can be re-scaled and shifted via the formula to convert it to the "standard" normal distribution. This variate is also called the standardized form of
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok.
Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky
použitia.






































